Difference Between IP54 and IP65 Environmental Test Equipment
Difference Between IP54 and IP65 Environmental Test Equipment
Understanding ingress protection ratings becomes essential when selecting environmental test equipment, as these ratings indicate how well enclosures resist intrusion from dust and liquids according to the International Electrotechnical Commission standard IEC 60529. IP54 and IP65 represent distinct protection levels with different testing requirements. IP54 test equipment offers limited dust ingress protection combined with splash water resistance, making it suitable for indoor or sheltered applications. IP65 equipment provides complete dust-tight protection alongside resistance to low-pressure water jets from any direction, designed for harsher outdoor environments. The testing methodologies, nozzle configurations, water pressure parameters, and equipment complexity vary significantly between these two ratings, influencing cost considerations and application suitability.

Fundamental Purpose: Splash Protection vs. Low-Pressure Jet Protection
Water Ingress Protection Level Comparison
IP54 equipment tests against water splashing from any direction, whereas IP65 equipment evaluates protection against low-pressure water jets projected from any angle. The fourth digit "4" in IP54 signifies splash protection, meaning water splashing against the enclosure from any direction shall have no harmful effect. The fifth digit "5" in IP65 indicates water jet protection, requiring the enclosure to withstand directed water streams under specific pressure conditions. This fundamental difference affects test chamber design, water delivery systems, and validation criteria.
Dust Protection Capabilities
The first numeral in IP ratings refers to protection against solid objects, rated from 0 (no protection) to 6 (no ingress of dust). IP54's first digit "5" means limited dust ingress protection - while dust may enter the enclosure, it cannot accumulate in quantities that would interfere with equipment operation. IP65's first digit "6" designates complete dust-tight protection, meaning absolutely no dust particles can penetrate the enclosure under test conditions. This distinction becomes crucial for products deployed in dusty industrial environments, mining operations, or desert climates.
Application Environment Considerations
IP54 certification suits products intended for controlled indoor environments, commercial spaces, or areas with overhead protection from direct weather exposure. IP65 devices are predominantly used in exposed outdoor areas, while IP54 finds applications in homes, offices, and commercial spaces with limited exposure to dust and water. The equipment selection impacts product reliability, warranty claims, and customer satisfaction across different deployment scenarios.
Comparing Nozzle Design: Oscillating vs. Fixed 6.3mm Jet Nozzle
IP54 Spray Nozzle Specifications
IP54 test equipment employs oscillating spray nozzles or counterbalanced shields with perforations. The oscillating nozzle features a counterbalanced U-shaped shield with holes measuring approximately 0.4mm diameter, spaced 50mm apart. During testing, this shield oscillates through an arc, simulating water splashing from various angles. The water delivery system operates without significant pressure requirements, focusing on coverage rather than force. This design allows comprehensive surface exposure while maintaining relatively simple hydraulic systems.
IP65 Jet Nozzle Configuration
IP65 testing requires water to be projected through a 6.3mm internal diameter nozzle at 12.5 liters per minute flow rate with 30 kPa pressure from a 3-meter distance for at least 15 minutes. The fixed nozzle design concentrates water into a coherent jet stream, simulating cleaning operations, heavy rain conditions, or wave splash scenarios. The nozzle remains stationary while the test specimen rotates on a turntable, ensuring complete circumferential coverage. This precision-engineered nozzle must maintain consistent flow characteristics throughout extended test durations.
Testing Methodology Differences
IP54 testing involves positioning the specimen within the spray envelope using appropriate IP54 test equipment, rotating it slowly to ensure all surfaces receive water exposure during the minimum 10-minute test duration. IP65 testing requires precise distance control between nozzle and specimen, systematic angular positioning to verify all surfaces withstand jet pressure, and extended duration to validate seal integrity under sustained hydraulic stress. These methodological differences demand distinct chamber designs and control systems.
How Water Pressure and Flow Rate Specifications Differ?
IP54 Water Pressure Requirements
IP54 testing operates at minimal pressure levels, typically ranging from 50 to 150 kPa depending on the spray head design and test distance. The water delivery system prioritizes uniform distribution rather than forceful impact. Flow rates typically range between 0.07 liters per minute per hole in oscillating spray shields, with total flow dependent on the number of perforations and shield size. This low-pressure approach simulates natural rainfall, incidental splashing from nearby water sources, or condensation dripping scenarios.
IP65 Pressure and Flow Specifications
The IP65 rating requires testing with 12.5 liters of water volume per minute for at least 15 minutes under 30 kPa pressure delivered from a 3-meter distance. This specification translates to approximately 187.5 liters total water consumption per standard test cycle. The higher pressure generates kinetic energy sufficient to challenge seal designs, gasket compression, and thread engagement quality. The sustained jet stream tests not only immediate water exclusion but also seal fatigue resistance over the test period.
Hydraulic System Complexity Comparison
Parameter | IP54 Test Equipment | IP65 Test Equipment |
Water Pressure | 50-150 kPa | 30 kPa (at nozzle) |
Flow Rate | 0.07 L/min per hole | 12.5 L/min ±5% |
Nozzle Diameter | 0.4mm (multiple holes) | 6.3mm (single jet) |
Test Distance | Variable (close range) | 2.5-3 meters |
Test Duration | 10 minutes minimum | 15 minutes minimum |
Water Consumption | Approximately 20-40L | Approximately 187.5L |
The table illustrates how IP65 equipment demands more robust pumping systems, precise flow regulation, and larger water supply capacity compared to IP54 configurations.
Equipment Complexity: Simple Spray Tray vs. High-Pressure Pump System
IP54 Chamber Components
IP54 test equipment features relatively straightforward construction with basic components including a water reservoir, low-pressure circulation pump, oscillating spray mechanism, specimen turntable, and drainage system. The control system manages rotation speed, spray duration, and water temperature if specified. Chamber dimensions can remain compact since spray distance requirements are minimal. The oscillating mechanism typically employs simple motor-driven linkages or cam systems to achieve the rocking motion. Total power consumption remains modest, often below 2kW for standard laboratory configurations.
IP65 Chamber Infrastructure
IP65 test equipment demands sophisticated engineering with high-capacity water storage tanks, high-pressure booster pumps capable of sustaining 30 kPa at the required flow rate, precision flow meters with ±5% accuracy, pressure regulators, programmable specimen turntables with variable speed and angular positioning, and often water purification systems to prevent nozzle clogging. The chamber must accommodate the 3-meter jet distance while providing adequate space for specimen rotation. Programmable color LCD touch screen controllers enable precise parameter setting, test sequencing, and data logging. Ethernet connectivity allows integration with laboratory management systems and remote monitoring capabilities.
Cost and Space Considerations
The enhanced capabilities of IP65 test equipment translate to significantly higher capital investment, typically ranging from 150% to 300% of comparable IP54 chamber costs. Floor space requirements expand proportionally due to jet distance specifications and larger water storage needs. Operating costs increase through higher water consumption, greater electrical demand for pump operation, and more frequent calibration requirements to maintain flow and pressure accuracy within specification tolerances.
Understanding the Test Duration and Coverage Area Requirements
IP54 Test Duration Standards
Standard IP54 testing requires a minimum 10-minute exposure period with the oscillating spray system operating continuously. The specimen must complete multiple rotations during this interval, ensuring all surfaces receive adequate water exposure. Some test protocols specify particular rotation speeds, typically between 1-4 revolutions per minute, to guarantee systematic coverage without creating centrifugal forces that might deflect water spray patterns. Temperature monitoring throughout the test ensures consistency, as water viscosity affects spray characteristics.
IP65 Test Duration Requirements
IP65 testing mandates at least 15 minutes of continuous water jet exposure at the specified pressure and flow rate. The extended duration serves multiple validation purposes: confirming immediate water exclusion, evaluating seal resilience under sustained pressure, detecting progressive water migration through thread paths or compression joint interfaces, and identifying potential accumulation points where water might eventually penetrate. The specimen must be repositioned multiple times during testing to ensure the jet impacts all critical surfaces and joint lines.
Coverage Area Verification
Test Aspect | IP54 Requirements | IP65 Requirements |
Minimum Duration | 10 minutes | 15 minutes |
Specimen Rotation | Continuous, 1-4 RPM | Systematic positioning |
Surface Coverage | Omnidirectional spray | Targeted jet exposure |
Critical Zones | All external surfaces | Seams, joints, penetrations |
Post-Test Inspection | Visual examination | Detailed internal inspection |
The table demonstrates how IP65 testing involves more rigorous evaluation protocols, including post-test teardown inspection to verify no water penetration occurred even if external appearance suggests proper sealing.
Choosing Between Dust and Limited Dust vs. Complete Dust Protection
IP5X Limited Dust Ingress Protection
The "5" rating means dust-protected rather than dust-tight. Under controlled test conditions involving talcum powder in a vacuum chamber, some dust particles may enter the enclosure, but the quantity cannot be sufficient to interfere with equipment operation or safety. Using specialized IP54 test equipment, this level proves adequate for electronics housed within buildings, automotive interior components, or devices with internal air circulation that can tolerate minimal particle intrusion. The test involves creating a vacuum condition within a dust-laden chamber, typically maintaining depression of up to 2 kPa for 2-8 hours depending on enclosure volume.
IP6X Complete Dust-Tight Certification
The "6" rating requires absolute dust exclusion. No visible dust accumulation is permitted inside the enclosure following extended exposure in a dust-laden environment under vacuum conditions. This protection level becomes mandatory for sensitive optical systems, precision measurement instruments, medical devices, or equipment deployed in extreme environments like mines, cement plants, or agricultural dust storms. Testing involves more stringent vacuum depression and longer duration to prove comprehensive sealing effectiveness.
Testing Equipment Differences
Dust Protection Feature | IP5X Test Setup | IP6X Test Setup |
Dust Chamber Required | Standard vacuum chamber | Enhanced seal verification |
Test Duration | 2-8 hours based on volume | 8 hours minimum |
Vacuum Depression | Up to 2 kPa | Up to 2 kPa sustained |
Dust Medium | Talcum powder | Talcum powder |
Pass Criteria | Limited ingress acceptable | Zero ingress required |
Post-Test Evaluation | Operational functionality | Visual and functional |
The distinction in dust protection requirements influences chamber sealing design, gasket selection, cable entry specifications, and overall manufacturing precision, all of which affect test equipment configuration and cost.
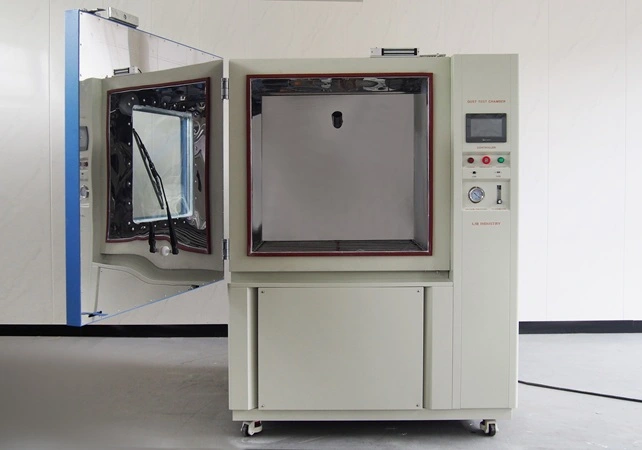
LIB IP54 Test Equipment: Precision Engineering for Specific Needs
LIB Industry delivers comprehensive IP54 test equipment solutions engineered for accuracy and reliability.
Technical Capabilities Overview
The LIB IP54 Test Equipment integrates IPX3, IPX4, IPX5, and IPX6 testing capabilities within a unified chamber platform, offering exceptional versatility for laboratories requiring multiple ingress protection validation levels. The Model RD-1200C features chamber capacities ranging from 800L to 2000L and beyond, accommodating diverse specimen sizes from small electronic components to large industrial enclosures. The programmable color LCD touch screen controller provides intuitive operation with preset test sequences, customizable parameters, and comprehensive data logging. Ethernet connectivity enables seamless integration with laboratory information management systems, supporting quality assurance documentation requirements and regulatory compliance reporting.
Design Excellence and Safety Features
The chamber construction employs SUS304 stainless steel interior surfaces, ensuring corrosion resistance and longevity even with continuous water exposure. Double-layer insulating glass observation windows with integrated wipers allow uninterrupted test monitoring while maintaining chamber integrity. The turntable system, machined from 304 stainless steel, supports loads up to 20kg with adjustable rotation speed from 0-7 RPM, enabling precise angular positioning for comprehensive surface coverage. Safety systems include over-temperature protection, over-current protection, water shortage protection, earth leakage protection, and phase sequence protection, ensuring operator safety and equipment preservation.
Application Versatility
LIB IP54 test equipment serves diverse industries including lighting manufacturers validating outdoor luminaire seals, electrical cabinet producers certifying industrial control panel protection, automotive suppliers testing component weather resistance, and consumer electronics companies verifying device durability. The equipment complies with IEC 60529, ISO 20653, and MIL-STD-810 standards, providing internationally recognized certification testing. The built-in water tank, booster pump, automatic water supply system, and water purification system create a self-contained testing platform requiring minimal external infrastructure. The customizable chamber dimensions and test parameters accommodate unique customer specifications, from specialized nozzle configurations to modified spray patterns for non-standard validation requirements.
Conclusion
Selecting between IP54 and IP65 test equipment demands careful evaluation of product application environments, protection requirements, and budget constraints. IP54 equipment provides cost-effective validation for splash protection scenarios, while IP65 systems deliver rigorous jet resistance certification for harsh outdoor deployments. Understanding the technical distinctions - from nozzle design and hydraulic specifications to dust protection levels and testing duration - enables informed equipment procurement decisions aligned with certification objectives and quality assurance standards.
FAQs
Can IP54 rated products be used outdoors?
IP54 products can function in sheltered outdoor locations with overhead protection from direct weather exposure. However, they remain vulnerable to sustained rain or water jets. Consider IP65 or higher ratings for fully exposed outdoor installations requiring reliable performance across diverse weather conditions and cleaning scenarios.
How long does IP54 vs IP65 certification testing take?
IP54 testing requires a minimum 10-minute continuous spray exposure with specimen rotation, while IP65 testing mandates at least 15 minutes of sustained water jet application from multiple angles. Total testing time includes setup, conditioning, exposure, drainage, and post-test inspection, typically spanning 45-90 minutes per specimen depending on complexity.
What maintenance does IP test equipment require?
Regular maintenance includes nozzle inspection and cleaning to prevent flow restriction, flow meter calibration verification quarterly, turntable bearing lubrication, water system disinfection to prevent biological growth, gasket replacement on chamber doors, and annual pressure gauge certification. Proper maintenance ensures consistent test accuracy and equipment longevity throughout operational life.
As a leading IP54 test equipment manufacturer and supplier, LIB Industry provides turnkey environmental testing solutions tailored to your specifications. Contact us at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss your ingress protection testing requirements and discover how our precision-engineered chambers can elevate your quality assurance capabilities.