Understanding ASTM B117 Requirements for Salt Spray Fog Test Chambers
Understanding ASTM B117 Requirements for Salt Spray Fog Test Chambers
ASTM B117 serves as the definitive international standard governing neutral salt spray testing procedures, establishing precise protocols for evaluating corrosion resistance in metallic coatings and surface treatments. Many laboratories conduct these assessments using a salt spray fog test chamber, which provides the controlled environment required to meet the standard’s specifications. This standardized methodology ensures reproducible, comparable results across laboratories worldwide by specifying exact parameters for chamber design, solution preparation, temperature control, and exposure conditions. Mastering these requirements proves essential for manufacturers seeking to validate product durability, meet regulatory compliance, and deliver reliable quality assurance data to stakeholders throughout automotive, aerospace, marine, and construction industries.

Key Provisions of ASTM B117 Standard
Testing Environment Specifications
The standard mandates maintaining a precisely controlled atmosphere within the test enclosure. Chamber temperature must stabilize at 35°C ± 2°C throughout the exposure zone, measured at locations where specimens reside. This thermal consistency prevents localized variations that could skew corrosion rates and compromise data integrity.
Solution Preparation Requirements
ASTM B117 specifies a neutral salt solution containing 5% sodium chloride by mass, prepared using distilled or deionized water meeting specific purity criteria. The solution pH must range between 6.5 and 7.2 when measured at 25°C, ensuring neutral conditions that avoid acidic or alkaline bias in corrosion mechanisms.
Spray Collection Rate Standards
The protocol establishes fog deposition rates between 1.0 to 2.0 ml per 80 cm² surface area per hour. This quantifiable metric ensures adequate salt exposure without excessive solution accumulation that might create unrealistic testing conditions or dilute the corrosive medium.
Required Chamber Specifications and Design Criteria
Construction Materials and Corrosion Resistance
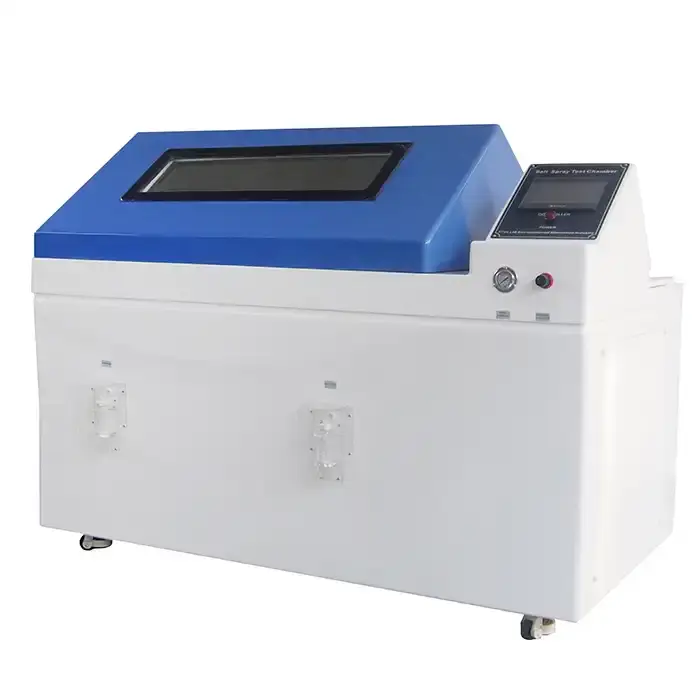
Salt spray fog test chambers constructed from glass fiber reinforced plastics deliver superior performance versus metallic alternatives. These materials withstand continuous salt fog exposure without degradation, preventing contamination from chamber corrosion that could invalidate test results. The single-piece molded construction eliminates seams where corrosion might initiate.
Transparent Observation Capabilities
Chamber lids fabricated from transparent resin materials enable visual monitoring without interrupting test cycles. This design feature allows quality control personnel to inspect specimen conditions, verify fog density, and confirm proper spray distribution throughout exposure periods while maintaining environmental isolation.
Spray Generation System Architecture
The atomization system comprises specialized nozzles producing uniform fog particles within specified size ranges. Properly designed spray towers create turbulent mixing patterns that distribute salt-laden mist evenly throughout the test volume, preventing concentration gradients that compromise reproducibility.
Chamber Component | Material Specification | Performance Requirement |
Main Body | Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastics | Corrosion-resistant, one-piece molding |
Observation Lid | Transparent Resin | Chemical resistance, optical clarity |
Heating Elements | Nichrome Alloy | Uniform heat distribution, longevity |
Air Preheating Barrel | Corrosion-resistant Tank | 31L capacity, saturation function |
Test Duration, Temperature, and Solution Concentration Guidelines
Continuous Exposure Protocols
ASTM B117 permits both continuous and interrupted exposure schedules depending on evaluation objectives. Continuous testing typically extends from 24 hours to several hundred hours, with duration determined by coating thickness, material composition, and performance specifications. Extended cycles reveal long-term degradation patterns and failure mechanisms.
Temperature Monitoring and Control
Precision temperature sensors positioned throughout the exposure zone verify thermal uniformity within a salt spray fog test chamber. PTR platinum resistance thermometers with 0.001°C accuracy provide real-time feedback to programmable controllers, enabling automatic adjustments that maintain the mandated 35°C setpoint regardless of ambient fluctuations.
Solution Concentration Verification
Regular concentration checks using density measurements or titration methods confirm the 5% sodium chloride content remains within tolerance. Evaporation during extended testing can concentrate the solution, necessitating periodic replenishment with distilled water to restore proper salinity levels and maintain standardized conditions.
Parameter | ASTM B117 Requirement | Measurement Method |
Temperature | 35°C ± 2°C | PT100 RTD sensors |
Solution Concentration | 5% ± 0.1% NaCl | Density or titration |
pH Range | 6.5 - 7.2 at 25°C | Calibrated pH meter |
Fog Deposition Rate | 1.0 - 2.0 ml/80cm²·h | Collection cylinders |
Sample Placement and Exposure Rules
Specimen Positioning Requirements
Test samples must be oriented at angles between 15° and 30° from vertical, with coated surfaces facing upward to receive direct fog exposure. This angled placement prevents solution accumulation while ensuring adequate salt contact. Specimens should never touch chamber walls or other samples, maintaining independent exposure conditions.
Support Structure Configuration
Standardized support systems utilize non-metallic rods and V-shaped grooves that minimize contact points with test specimens. These configurations prevent crevice corrosion at support interfaces and allow unrestricted fog circulation around all exposed surfaces, ensuring representative corrosion patterns develop.
Spatial Distribution Considerations
Proper specimen spacing within the chamber prevents shadowing effects where fog density decreases behind upstream samples. Maintaining adequate clearances between specimens and from chamber walls ensures uniform exposure intensity across all test articles, eliminating positional bias in results.
Documentation and Reporting Requirements
Pre-Test Documentation Standards
Comprehensive records must detail specimen preparation methods, surface cleaning procedures, coating application techniques, and any pre-conditioning treatments. Dimensional measurements, surface finish characterizations, and photographic documentation establish baseline conditions for post-exposure comparisons.
Exposure Parameter Recording
Continuous monitoring systems document temperature profiles, spray cycle timing, solution pH measurements, and fog collection rates throughout test duration. Automated data logging provides verifiable evidence of standard compliance and enables statistical analysis of environmental stability.
Post-Exposure Evaluation Protocols
ASTM B117 requires systematic assessment of corrosion extent, including visual ratings, area calculations of corroded regions, and documentation of failure modes. Standardized rating scales facilitate objective comparisons between specimens and across different test campaigns.
Documentation Category | Required Information | Recording Frequency |
Specimen Details | Material, coating, dimensions, preparation method | Before testing |
Environmental Parameters | Temperature, pH, fog rate | Continuous/hourly |
Exposure Duration | Start time, end time, interruptions | Per test cycle |
Corrosion Assessment | Rating scale, area measurements, photographs | After exposure |
Ensuring Compliance with ASTM B117 for Accurate Testing
Equipment Calibration Procedures
Regular calibration of temperature sensors, pH meters, and solution concentration measurement devices in a salt spray fog test chamber maintains measurement accuracy and traceability to national standards. Calibration intervals typically range from quarterly to annually depending on equipment criticality and usage intensity.
Operational Verification Checks
Daily operational checks verify spray nozzle function, fog uniformity, and heating element performance before commencing test cycles. These preventive measures identify equipment malfunctions that could invalidate expensive, time-consuming test programs and compromise quality assurance data.
Inter-Laboratory Comparison Testing
Participating in round-robin testing programs validates chamber performance against peer facilities worldwide. These comparative exercises identify systematic biases and confirm that equipment modifications or operational variations don't introduce non-standard results.
Simplify ASTM B117 Compliance with LIB Industry's Precision Salt Spray Fog Test Chamber
Advanced Control Systems Integration
LIB Industry chambers incorporate programmable color LCD touchscreen controllers with Ethernet connectivity and PC linking capabilities. These sophisticated interfaces enable remote monitoring, automatic data logging, and precise parameter adjustments that ensure continuous standard compliance without constant operator intervention.
Comprehensive Safety Architecture
Multiple protection systems including dry-combustion prevention, over-temperature cutoffs, over-current protection, refrigerant high-pressure monitoring, water shortage detection, and earth leakage protection safeguard both equipment and personnel. These redundant safety features minimize downtime and prevent damage from operational anomalies.
Flexible Configuration Options
Available models ranging from 110L to 1030L internal volumes accommodate diverse specimen sizes and testing throughput requirements. The modular design permits custom configurations matching specific application needs while maintaining full ASTM B117 compliance across all capacity ranges.
Conclusion
ASTM B117 compliance demands meticulous attention to chamber specifications, environmental parameters, and procedural details that collectively ensure reproducible corrosion testing results. Understanding these requirements enables manufacturers to select appropriate equipment, develop robust testing protocols, and generate reliable data supporting product development and quality assurance objectives across corrosion-sensitive industries worldwide.
FAQs
What is the primary difference between ASTM B117 and other salt spray standards?
ASTM B117 specifies neutral salt spray testing at pH 6.5-7.2, while alternatives like ASTM G85 encompass acidified, cyclic, and other modified fog conditions. The neutral protocol represents the most widely adopted baseline corrosion evaluation method globally.
How frequently should salt solution be replaced in ongoing tests?
Solution replacement intervals depend on contamination levels and concentration drift. Generally, weekly replacement maintains consistency during extended exposures, though continuous monitoring enables condition-based changeouts when pH or concentration exceeds tolerance limits.
Can ASTM B117 testing predict real-world service life accurately?
Salt spray testing provides accelerated corrosion exposure revealing comparative performance between materials and coatings. However, correlation with actual field conditions requires empirical validation since environmental factors like UV exposure, temperature cycling, and mechanical stress differ significantly from laboratory protocols.
Partner with LIB Industry for ASTM-Compliant Testing Solutions
LIB Industry stands as a trusted salt spray fog test chamber manufacturer and supplier, delivering precision-engineered equipment meeting international standards. Contact our technical specialists at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss customized testing solutions tailored to your specific corrosion evaluation requirements.