Why Salt Spray Testing Matters for Paints and Coatings?
Why Salt Spray Testing Matters for Paints and Coatings?
Salt spray testing plays a vital role in confirming the strength and quality of paints and coatings. Manufacturers use advanced equipment like the salt spray test chamber to simulate harsh environments and assess product performance. Industries such as automotive, marine, and aerospace rely on these tests to prevent corrosion.
Salt Spray Testing Basics
Corrosion Simulation
Salt spray testing simulates the harsh conditions that paints and coatings face in real life. In this process, technicians place samples inside a chamber where a fine mist of saltwater covers the surfaces. The chamber maintains a controlled temperature and high humidity, creating an environment that accelerates corrosion. This method helps manufacturers see how coatings perform when exposed to salty air, similar to what products experience near oceans or on winter roads.
Researchers have shown that corrosion simulation works well for testing coating durability. They use cycles of UV light and salt spray to mimic years of environmental exposure in just a few days. During these tests, scientists measure changes in glossiness, color, water resistance, and adhesion. They also use advanced tools to check how well coatings protect against rust. Machine learning models built from these experiments can predict how coatings will degrade over time. These results confirm that salt spray testing gives reliable information about how long a coating will last.
Testing Principles
Salt spray testing relies on scientific principles that replicate real-world corrosion. When metal surfaces meet salt mist, they start to oxidize, forming rust. The speed and amount of corrosion depend on the type of metal, the coating used, and the test conditions. The chamber uses a sodium chloride solution to create a steady, corrosive environment.
Standardized methods, such as ASTM B117, guide how to run these tests and interpret the results. Technicians measure corrosion rates and check for visible damage after set periods, sometimes up to 20 days. They also look at special coatings, like superhydrophobic layers, which repel water and resist rust. By comparing test results, manufacturers can choose the best coatings for different environments and ensure their products meet industry standards.
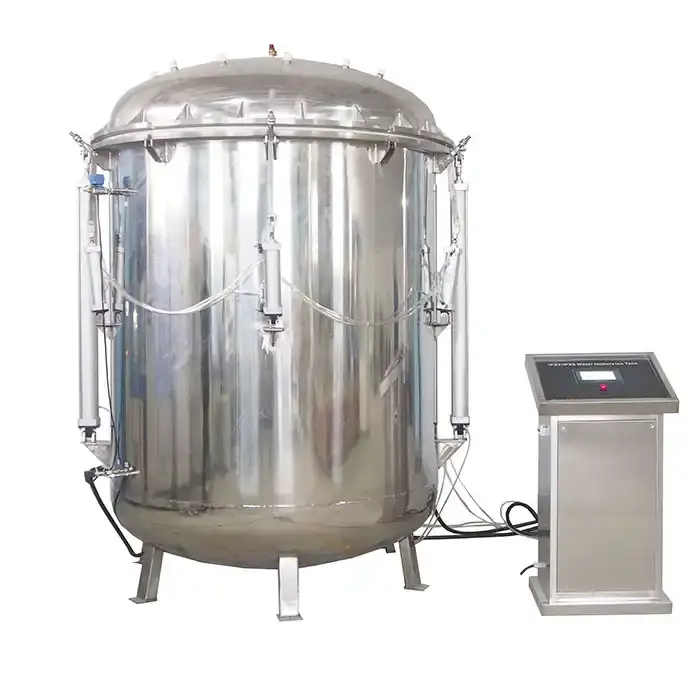
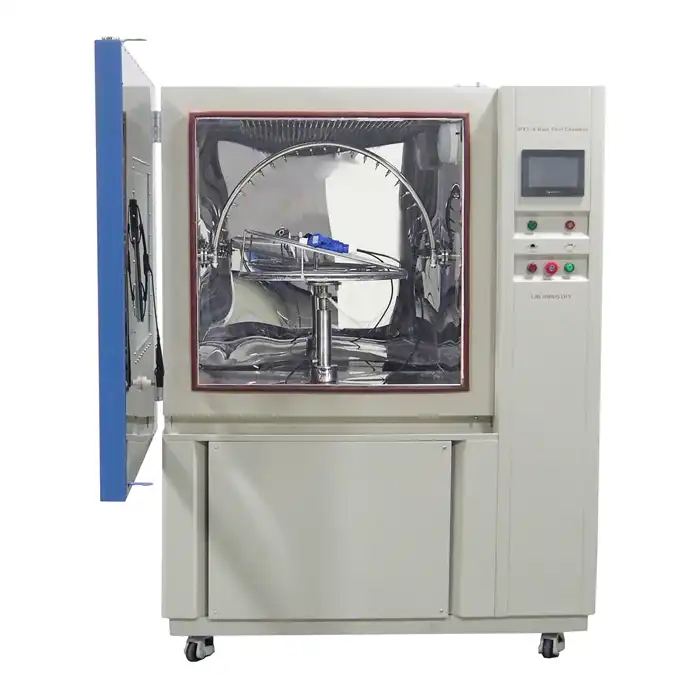
Salt Spray Test Chamber
Equipment Features
LIB Industry's salt spray test chamber stands out as a reliable and versatile solution for corrosion testing. This chamber helps manufacturers test the durability of paints and coatings under harsh conditions. It meets the needs of industries such as automotive, aerospace, marine, and electronics.
- The chamber uses a temperature control system with an installed heater. This system keeps the temperature steady, simulating different climates. The chamber can reach up to 60°C, which matches many real-world environments.
- A humidity control system keeps the air inside the chamber very moist. High humidity levels, between 95% and 98% RH, help speed up corrosion and make the test more accurate.
- The chamber supports both continuous and cyclic testing. Cyclic tests can include wetting, drying, and even SO2 gas injection. These cycles mimic changing weather and environmental conditions.
- The spray system uses an adjustable spray tower and nozzles. This setup creates a fine, even salt fog that covers all test samples. The salt fog sedimentation rate is carefully measured to ensure consistent results.
- The chamber holds samples at specific angles. This placement ensures every sample gets the same exposure to the salt spray.
- The chamber is built from glass fiber reinforced plastics. This material resists corrosion and lasts a long time, even with frequent use.
- Safety features include over-temperature protection, dry-combustion protection, and earth leakage protection. These features keep users and samples safe during long tests.
- The chamber comes in sizes from 110L to 1600L. This range allows users to test small or large batches of samples at once.
- The user-friendly interface lets technicians set and adjust test parameters easily. Proper calibration and regular monitoring keep the chamber running smoothly and ensure accurate results.
Industry Standards
The salt spray test chamber from LIB Industry complies with major international standards. ASTM B117 and ISO 9227 set strict rules for how salt spray tests should be done. These standards cover everything from chamber construction and temperature control to salt solution concentration and test duration.
ASTM B117 describes the standard practice for operating salt spray apparatus. It includes detailed procedures, equipment requirements, and acceptance criteria. ISO 9227 provides similar guidelines for corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres. Both standards require regular calibration and validation of the chamber. This ensures the chamber maintains the right temperature, humidity, and salt concentration throughout each test.
By meeting these standards, the salt spray test chamber gives manufacturers confidence in their test results. The chamber's ability to maintain stable conditions and provide repeatable results makes it a trusted tool for quality control and product development.
Benefits for Paints and Coatings
Durability Assessment
Salt spray testing helps manufacturers find weaknesses in paints and coatings before products reach the market. By exposing samples to a controlled salt fog, engineers can see how coatings respond to harsh environments. This process reveals early signs of rust, blistering, or peeling. When a coating fails, the test shows exactly where and how the problem starts. Product designers use this information to improve paint formulas and application methods.
Long-term studies by organizations like the U.S. Army Tank Automotive and Armaments Command and the automotive industry show that salt spray testing provides reliable data on coating durability. These studies use accelerated corrosion tests, such as the GM 9540P protocol, to measure how different paint systems perform over time. Researchers found that coating performance depends on factors like the type of metal, surface preparation, and how the paint is applied. By testing many samples across different labs, they observed consistent patterns in how coatings fail, such as disbondment and scribe creep. Improved evaluation methods, like scraping panels before measurement, made the results even more dependable. These findings confirm that salt spray testing, especially when combined with other tests, helps predict and improve the long-term durability of paints and coatings.
Quality Control
Salt spray testing plays a key role in quality assurance for paints and coatings. It gives manufacturers clear data to check if products meet industry standards and customer expectations. The salt spray test chamber provides a controlled environment for these tests, ensuring repeatable and accurate results.
Category | Details / Examples |
Quality Assurance Metrics | - Blistering and Delamination: Indicates paint adhesion strength and durability. |
- Color and Gloss Retention: Measures paint's ability to maintain appearance under harsh conditions. | |
- Adhesion Strength: Evaluated by tape and cross-hatch tests to ensure paint does not flake or detach. | |
- Impact Resistance: Assesses paint toughness against chipping and cracking. | |
- Chemical Resistance: Tests paint's durability against oils, fuels, and cleaning agents. | |
Successful Case Studies | - Epoxy Coatings: Extended paint lifespan with no corrosion after 5 years of salt spray exposure. |
- Nano-Ceramic Technology: Enhanced water and salt repellency, maintaining pristine finish in coastal environments. | |
- Self-Healing Paints: Microcapsules release healing agents upon damage, reducing rust formation. | |
- Organic Coatings: Environmentally friendly with superior corrosion resistance, outperforming standard coatings. | |
Formulation Improvements | - Binder Optimization: Stronger adhesion to prevent peeling/flaking. |
- Additive Adjustment: Better edge coverage additives to prevent corrosion at vulnerable areas. | |
- Pigment Selection: Use of inert pigments to avoid discoloration and degradation. | |
- Application Techniques: Improved spraying methods for uniform coverage. | |
- Curing Processes: Ensuring complete curing to enhance durability. |
Manufacturers use these metrics to track product quality and make improvements. For example, they may adjust the binder or pigment in a paint formula to prevent flaking or discoloration. They also refine application and curing processes to boost durability. Case studies show that advanced coatings, such as nano-ceramic or self-healing paints, perform well in salt spray tests and last longer in tough environments.
Salt spray testing also helps companies meet regulatory requirements and build customer trust. Products that pass these tests often require less maintenance and have a longer lifespan. This leads to lower repair costs and higher satisfaction for end users.
Limitations and Alternatives
Real-World vs. Lab Testing
Salt spray testing offers a fast and controlled way to check how paints and coatings resist corrosion. However, this method does not always match what happens in real environments. In the lab, technicians use a steady salt fog and fixed temperature to speed up corrosion. Real-world conditions, such as sunlight, rain, and temperature swings, create more complex challenges for coatings.
Researchers have compared rapid laboratory tests with long-term outdoor exposure. For example, studies on magnesium-based coatings used both salt spray chambers and field sites near the ocean and inland. Scientists tracked how coatings performed over time using special tools. They found that lab tests and field tests both gave useful information about how coatings protect metal. However, lab tests sometimes missed slow changes that only show up after years outside.
The following table highlights the main differences:
Aspect | Salt Spray Testing (Accelerated) | Natural Exposure Testing (Real-World) |
Advantages | Controlled, repeatable, and fast. Finds weak spots quickly. | Shows true performance in real conditions. Gives long-term data. |
Limitations | Misses some real-world factors like UV light and temperature changes. May not show all types of corrosion. | Takes months or years. Hard to control all variables. Results can be harder to compare. |
Recommendations | Good for quick checks and comparing products. Works best with other tests. | Best for final validation. Combine with lab tests for a full picture. |
Other Corrosion Tests
Salt spray testing is not the only way to check for corrosion. Other tests help fill in the gaps and provide a more complete view. Humidity chamber testing, for example, exposes samples to high moisture without salt. This method checks how coatings handle damp air and condensation.
Some labs use cyclic corrosion tests. These tests switch between wet, dry, and sometimes UV light cycles. This approach better mimics changing weather. Modified salt spray tests can also use synthetic ocean water and UV exposure to get closer to real conditions.
Common corrosion test methods:
- Humidity chamber testing: Measures resistance to moisture and condensation.
- Cyclic corrosion testing: Simulates weather changes with wet and dry cycles.
- Field exposure testing: Places samples outdoors for months or years.
Each method has strengths and weaknesses. Using several tests together helps manufacturers choose the best coatings for different environments.
Salt spray testing plays a key role in verifying the durability and performance of paints and coatings. This process simulates real corrosion, helping manufacturers spot weaknesses early and avoid costly failures. Reliable equipment, such as the Salt Spray Test Chamber, ensures accurate and repeatable results. By following international standards and using controlled test conditions, companies can make informed decisions and improve product quality. Manufacturers who add salt spray testing to their quality control programs protect both their products and their reputation.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of salt spray testing?
Salt spray testing checks how well paints and coatings resist corrosion. Engineers use this method to predict product durability in harsh environments.
How long does a typical salt spray test last?
Test duration depends on the standard and product type. Most tests run from 24 hours to 1,000 hours. Some advanced tests can last up to 2,000 hours.
Which industries benefit most from salt spray testing?
Automotive, marine, aerospace, and electronics industries rely on salt spray testing. These sectors need strong coatings to protect products from rust and damage.
If you would like more information on LIB Industry salt spray test chambers, please contact us at ellen@lib-industry.com.