Evaluating Material Aging with Hot and Cold Chamber Experiments
Imagine your aerospace component, pharmaceutical tablet, or polymer part quietly aging under unseen forces—enduring sweltering heat, freezing cold, and fluctuating humidity long before it ever reaches its intended application. Hot and cold chamber experiments make this invisible journey visible, simulating extreme environmental conditions to uncover material weaknesses, structural risks, and long-term stability challenges before real-world use.
This performance is already being validated in laboratories worldwide. An engineering team using the TH-500 hot and cold chamber shared early feedback: “The chamber accurately replicates temperature cycles, and the results are consistent with our predicted degradation patterns. It gives us confidence in our material selections.” Such real-world confidence underscores the importance of controlled environmental testing in ensuring product reliability and longevity. Let’s explore how hot and cold chambers accelerate material aging, reveal critical degradation mechanisms, and guide quality and design decisions across industries.
Material aging poses significant challenges across industries, from pharmaceuticals to aerospace engineering. Hot and cold chamber experiments provide controlled environments where researchers can accelerate and evaluate material degradation processes that would otherwise take years to observe. These sophisticated testing systems replicate extreme temperature fluctuations, humidity variations, and environmental stressors, enabling manufacturers to predict product lifespan, identify failure points, and optimize material selection. By subjecting samples to accelerated aging protocols, engineers gain critical insights into mechanical properties, chemical stability, and structural integrity changes over time. This methodology has become indispensable for quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and innovation in material science, helping industries deliver reliable products that withstand real-world conditions throughout their intended service life.
How Environmental Conditions Accelerate Material Aging?Temperature Extremes and Molecular Breakdown
Materials exposed to temperature extremes experience accelerated molecular degradation. High temperatures increase molecular kinetic energy, causing polymer chains to break down faster, while low temperatures can induce brittleness in certain materials. Thermal cycling between these extremes creates expansion and contraction stresses that weaken structural bonds over time.
molecular kinetic energy, causing polymer chains to break down faster, while low temperatures can induce brittleness in certain materials. Thermal cycling between these extremes creates expansion and contraction stresses that weaken structural bonds over time.
Humidity's Role in Chemical Reactions
Moisture acts as a catalyst for numerous degradation mechanisms including hydrolysis, oxidation, and corrosion. When combined with temperature variations, humidity accelerates chemical reactions that compromise material integrity. High humidity environments facilitate water absorption in polymers, leading to dimensional changes and mechanical property loss.
Synergistic Effects of Combined Stressors
The simultaneous application of temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors creates synergistic degradation effects that surpass individual stressor impacts. This combined exposure more accurately represents real-world conditions where materials face multiple challenges concurrently, making chamber testing essential for realistic aging evaluation.
Key Metrics in Material Degradation StudiesMechanical Property Changes
Tensile strength, elongation at break, and flexural modulus serve as primary indicators of material degradation. These properties typically decline as aging progresses, with measurement intervals providing quantifiable data about degradation rates. Regular testing throughout exposure periods establishes degradation curves essential for lifespan predictions.
Property | Typical Impact | Measurement Method |
Tensile Strength | Decreases 15-40% | Universal Testing Machine |
Elongation at Break | Reduces significantly | Extensometry |
Surface Hardness | May increase or decrease | Shore Durometer |
Color Stability | Yellowing or fading | Spectrophotometry |
Chemical Composition Analysis
Spectroscopic techniques such as FTIR and Raman spectroscopy detect molecular-level changes in aged materials. These methods identify oxidation products, chain scission events, and additive migration, revealing degradation mechanisms that aren't visible through mechanical testing alone.
Physical Appearance Indicators
Visual changes including discoloration, cracking, chalking, and deformation provide immediate qualitative assessment of material condition. While subjective, these observations correlate with underlying chemical and mechanical degradation, offering quick screening capabilities before detailed analysis.
Simulating Long-term Usage with Temperature CyclingAccelerated Aging Protocols
Temperature cycling protocols compress years of natural aging into weeks or months. The Arrhenius equation forms the theoretical foundation, relating temperature increases to reaction rate acceleration. Typical protocols involve cycling between temperature extremes at specified rates and dwell times.
theoretical foundation, relating temperature increases to reaction rate acceleration. Typical protocols involve cycling between temperature extremes at specified rates and dwell times.
Cycle Design Considerations
Effective cycling protocols balance acceleration factors with material relevance. Ramp rates between 1-3°C per minute prevent unrealistic thermal shock while maintaining reasonable test durations. Dwell times at temperature extremes allow thermal equilibration and sufficient time for degradation mechanisms to progress.
Correlation with Field Performance
Establishing correlation factors between accelerated testing and actual field performance requires extensive validation. Historical field data combined with chamber testing results enables predictive modeling. Industries typically develop correlation coefficients specific to material types and application environments.
| Name | Hot and Cold Chamber | |||||
Model | TH-100 | |||||
Temperature range | -20℃ ~+150 ℃ | |||||
Low type | A: -40℃ B:-70℃ C -86℃ | |||||
Humidity Range | 20%-98%RH | |||||
Temperature deviation | ± 2.0 ℃ | |||||
Heating rate | 3 ℃ / min | |||||
Cooling rate | 1 ℃ / min | |||||
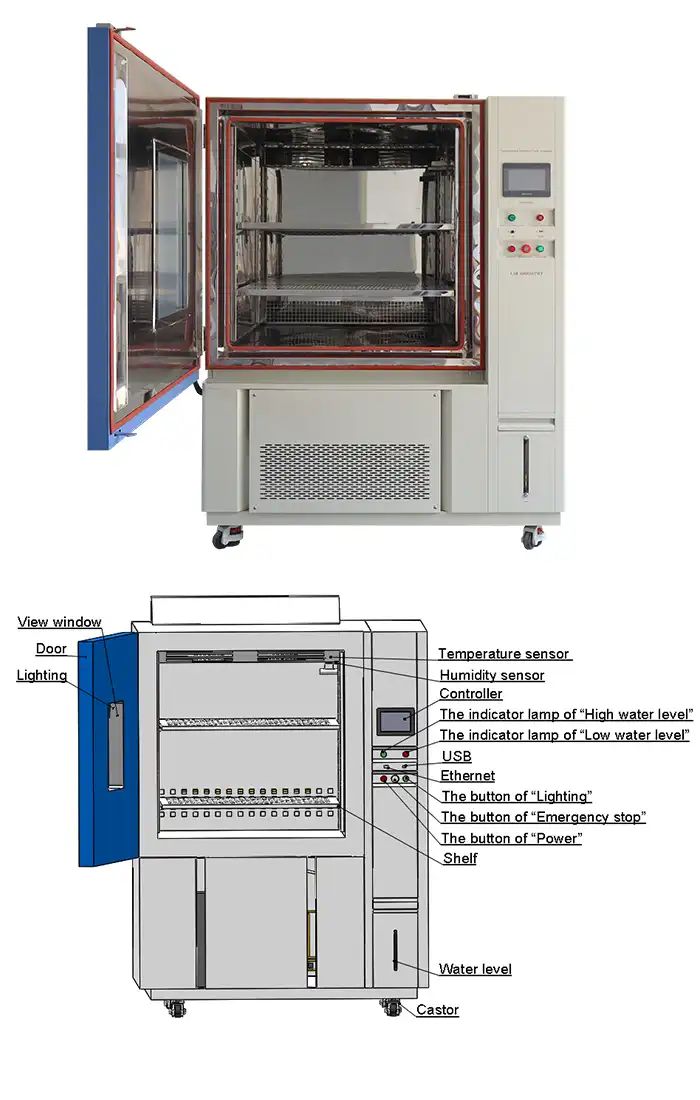
Controller | Programmable color LCD touch screen controller, Multi-language interface, Ethernet , USB | |||||
Exterior material | Steel Plate with protective coating | |||||
Interior material | SUS304 stainless steel | |||||
Standard configuration | 1 Cable hole (Φ 50) with plug; 2 shelves | |||||
Timing Function | 0.1~999.9 (S,M,H) settable | |||||
Effects of Humidity and Heat on Material PropertiesPolymer Degradation Mechanisms
Combined heat and humidity exposure triggers hydrolytic degradation in many polymers, particularly polyesters and polyamides. Water molecules attack ester linkages, causing chain scission and molecular weight reduction. This process manifests as embrittlement and loss of mechanical properties over extended exposure periods.
Metal Corrosion Acceleration
Elevated temperatures increase corrosion rates exponentially when moisture is present. The hot and cold chamber environment simulates coastal, tropical, or industrial atmospheres where metal components face simultaneous heat and humidity challenges. Protective coatings undergo similar accelerated degradation testing to verify their effectiveness.
Test Condition | Temperature Range | Humidity Range | Typical Duration |
Standard Stability | +40°C to +75°C | 75% RH | 6-12 months |
Accelerated Aging | -40°C to +150°C | 20-98% RH | 3-6 months |
Thermal Shock | -70°C to +150°C | Varied | 500-1000 cycles |
Composite Material Challenges
Composite materials present unique aging challenges as different constituent materials respond differently to environmental exposure. Matrix materials may degrade while reinforcing fibers remain intact, creating delamination and interface failure. Chamber testing reveals these complex interactions under controlled conditions.
Predictive Modeling for Material Lifespan

Mathematical Modeling Approaches
Time-temperature-superposition principles allow researchers to construct master curves from accelerated test data. These curves extrapolate short-term high-temperature data to predict long-term ambient temperature performance. Statistical models incorporating Weibull distributions account for variability in material response.
Data Collection and Analysis
Systematic data collection at predetermined intervals throughout chamber testing provides the foundation for accurate modeling. Multiple samples tested simultaneously reduce experimental error. Statistical software processes this data to generate confidence intervals and failure probability predictions.
Validation and Refinement
Predictive models require continuous refinement through comparison with actual field failures and long-term natural aging studies. Discrepancies between predictions and reality prompt model adjustments, improving accuracy for future predictions. This iterative process enhances reliability engineering practices.
Ensuring Material Reliability in Product ApplicationsQuality Assurance Integration
Hot and cold chamber testing integrates into comprehensive quality management systems, providing objective evidence of material suitability. Test results inform material specifications, supplier qualification processes, and incoming inspection criteria. This systematic approach minimizes field failures and warranty claims.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and automotive components face stringent regulatory requirements for stability testing. Chamber testing according to ICH guidelines, ISO standards, and industry-specific protocols demonstrates regulatory compliance. Documentation from these tests supports product registration and market approval processes.
Design Optimization Feedback
Aging test results guide design improvements by identifying vulnerable components and materials. Engineers use this information to specify alternative materials, add protective features, or modify designs to extend product lifespan. This feedback loop accelerates product development while reducing field failure risks.
Simulate Long-Term Aging Accurately with LIB Industry's Hot and Cold Chamber
Advanced Temperature Control Technology
LIB Industry's hot and cold chambers utilize French TECUMSEH compressors delivering precise temperature control from -70°C to +150°C with ±0.5°C fluctuation. Programmable color LCD touchscreen controllers with Ethernet connectivity enable complex cycling protocols and remote monitoring capabilities. The mechanical compression refrigeration system ensures reliable cooling performance throughout extended test campaigns.
Comprehensive Safety Features
Multiple protection systems safeguard both samples and equipment, including humidifier dry-combustion protection, over-temperature protection, over-current protection, and water shortage protection. The 304 stainless steel interior resists corrosion from moisture and temperature extremes, ensuring long-term chamber reliability and contamination-free testing environments.
Model | Interior Volume | Internal Dimensions (mm) | Temperature Range Options |
TH-100 | 100L | 400×500×500 | A: -20°C to +150°C |
TH-225 | 225L | 500×600×750 | B: -40°C to +150°C |
TH-500 | 500L | 700×800×900 | C: -70°C to +150°C |
TH-800 | 800L | 800×1000×1000 | Customizable ranges |
TH-1000 | 1000L | 1000×1000×1000 | Available upon request |
Turnkey Solution and Support
LIB Industry provides complete turnkey solutions encompassing research, design, production, commissioning, delivery, installation, and training. The three-year warranty, automatic water supply system, and door-to-door service ensure seamless integration into testing laboratories. Custom configurations accommodate specific testing requirements across pharmaceutical, food, research, and industrial applications.
Conclusion
Hot and cold chamber experiments have revolutionized material aging evaluation by compressing years of natural degradation into manageable testing periods. These controlled environments enable precise assessment of how temperature, humidity, and cycling stresses affect material properties over time. The resulting data drives informed decisions in material selection, product design, and quality assurance across industries. As materials become increasingly sophisticated and applications more demanding, chamber testing remains the cornerstone of reliability engineering. Investing in quality testing equipment and rigorous protocols ensures products meet performance expectations throughout their intended lifespan, protecting both manufacturers and end-users from premature failures.
FAQs
What temperature cycling rate is most appropriate for polymer aging studies?
Most polymer aging studies employ cycling rates between 1-3°C per minute to prevent thermal shock while maintaining reasonable test durations. Slower rates better simulate natural environmental transitions, while faster rates accelerate testing. The optimal rate depends on material glass transition temperature and intended application conditions.
How do I correlate accelerated chamber testing with actual field performance?
Correlation requires establishing acceleration factors through the Arrhenius equation combined with field failure data. Testing at multiple temperatures creates data points for extrapolation. Validation involves comparing predicted lifespans with actual field performance over several years, adjusting correlation coefficients as needed.
Can hot and cold chambers test multiple material types simultaneously?
Yes, chambers can test multiple materials simultaneously provided they require similar environmental conditions. Separate shelving accommodates different sample types. However, materials with vastly different testing requirements or those that might contaminate others should be tested in separate runs to maintain data integrity.
Ready to evaluate your materials' long-term performance? Contact LIB Industry, a leading hot and cold chamber manufacturer and supplier, for customized environmental testing solutions. Our experts provide comprehensive support from equipment selection through installation and training. Reach us at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss your specific testing requirements.