How Accelerated Weathering Tests Help Reduce Product Failure Risks?
Accelerated weathering tests provide manufacturers with a controlled method to simulate years of outdoor exposure in just weeks or months, revealing potential material weaknesses before products reach the market. By exposing materials to intense light, heat, and moisture cycles using equipment like xenon arc weatherometers, companies can identify degradation patterns that lead to cracking, fading, discoloration, and structural failure. This proactive approach allows engineers to validate material choices, optimize formulations, and implement design changes early in development, significantly reducing the likelihood of costly field failures, warranty claims, and reputation damage while ensuring products meet durability expectations throughout their intended service life.
What Failure Modes Can Accelerated Weathering Reveal Early?
Accelerated weathering chambers excel at uncovering multiple degradation mechanisms that compromise product integrity over time. Understanding these failure modes enables manufacturers to address vulnerabilities before
mass production begins.
Photodegradation and Color Stability Issues
UV radiation breaks down polymer chains and chromophores in materials, causing yellowing, chalking, and loss of mechanical properties. Xenon arc weatherometers replicate the full solar spectrum, particularly the critical 300-400nm bandwidth where most photochemical reactions occur. Testing under controlled irradiance levels reveals whether coatings, plastics, or textiles will maintain acceptable appearance and performance after prolonged sun exposure.
Thermal Cycling Stress and Dimensional Changes
Temperature fluctuations between -40°C and 100°C simulate diurnal heating and nighttime cooling that materials experience outdoors. These cycles expose coefficient of thermal expansion mismatches between substrates and coatings, leading to delamination, cracking, or warping. Black panel temperature monitoring ensures test conditions accurately reflect real-world surface heating on dark-colored products.
Moisture-Induced Degradation Pathways
Humidity cycling between 30% and 98% RH combined with water spray functions replicates dew formation, rain exposure, and moisture absorption effects. Hygroscopic materials may swell, plasticizers can leach out, and corrosion may initiate at vulnerable interfaces. Testing moisture sensitivity early prevents blistering, adhesion loss, and biological growth issues that develop during outdoor service.
Failure Mode | Primary Cause | Typical Symptoms | Industries Most Affected |
Photodegradation | UV radiation exposure | Color fading, chalking, gloss loss | Automotive, textiles, coatings |
Thermal stress | Temperature cycling | Cracking, warping, delamination | Building materials, electronics |
Moisture damage | Water absorption and humidity | Swelling, corrosion, adhesion failure | Marine applications, outdoor furniture |
Linking Weathering-Induced Degradation to Field Performance Risks
Translating laboratory test results into real-world failure predictions requires understanding correlation factors between accelerated conditions and actual service environments.
Establishing Acceleration Factors for Different Climates
The relationship between xenon arc weatherometers hours and outdoor exposure months varies by geographic location, season, and mounting orientation. Materials tested at 150W/m² irradiance may experience acceleration factors ranging from 3:1 to 8:1 compared to typical outdoor conditions. Calibrated radiometers with ±5% tolerance ensure consistent energy delivery, while programmable controllers allow simulation of specific climate profiles matching target markets.
Identifying Critical Degradation Thresholds
Rather than testing to complete failure, engineers establish performance criteria that define acceptable end-of-life conditions. Color change limits, minimum retained tensile strength percentages, or maximum gloss reduction values serve as pass/fail criteria. By monitoring these parameters throughout exposure cycles, teams determine when materials approach critical thresholds that signal impending field failures.
Validating Laboratory Predictions with Field Exposure
Parallel testing programs that expose identical samples both in weathering chambers and outdoor test sites verify correlation accuracy. Florida, Arizona, and other high-intensity locations provide natural exposure benchmarks. Comparing degradation rates between laboratory and field samples refines predictive models and builds confidence in accelerated test protocols.
How Xenon Arc Testing Supports Predictive Reliability Engineering?
Integration of weathering data into reliability frameworks transforms testing from quality control checkpoints into strategic product development tools.
Generating Survival Probability Models
Statistical analysis of multiple sample failures across different exposure durations produces Weibull distributions or other survival curves. These models predict the percentage of products expected to fail after specific service periods under defined environmental conditions. Design teams use this probabilistic information to establish warranty periods and maintenance schedules.
Optimizing Material Formulations Through DOE Approaches
Design of experiments methodology combined with accelerated weathering enables systematic evaluation of formulation variables. Testing matrix variations in stabilizer packages, pigment types, or polymer blends reveals which combinations maximize durability. This data-driven optimization reduces development cycles compared to trial-and-error approaches.
Supporting Root Cause Analysis of Field Failures
When unexpected failures occur after product launch, xenon arc weatherometers recreate suspected environmental stress combinations. Engineers can test whether observed damage patterns match those produced under specific temperature, humidity, and UV exposure sequences. This diagnostic capability accelerates identification of failure mechanisms and supports corrective action development.
Testing Parameter | Standard Range | Application Impact |
Irradiance level | 150W/m² (300-400nm) | Controls photodegradation rate |
Chamber temperature | -40°C to 100°C | Simulates thermal stress extremes |
Black panel temperature | 35°C to 85°C | Represents actual surface heating |
Humidity range | 30% to 98% RH | Replicates moisture exposure cycles |
Sample rotation speed | 1 rpm | Ensures uniform exposure distribution |
Reducing Warranty Claims Through Early Material Validation
Proactive weathering assessment directly impacts financial performance by preventing expensive post-launch quality issues.
Quantifying Cost Avoidance from Prevented Failures
A single product recall or widespread warranty claim event can cost millions in replacement parts, labor, shipping, and reputation damage. Investing several thousand dollars in comprehensive weathering validation during development prevents these exponential costs. Case studies across automotive and construction industries demonstrate return on investment ratios exceeding 100:1 for properly executed testing programs.
Establishing Evidence-Based Warranty Periods
Rather than selecting warranty durations based on competitive pressures or arbitrary timeframes, manufacturers use weathering data to set defensible coverage periods. If testing demonstrates that 95% of samples retain critical properties after simulated five-year exposure, companies can confidently offer matching warranty terms. This evidence-based approach balances customer protection with financial risk management.
Differentiating Products Through Verified Durability Claims
Marketing teams leverage verified weathering performance as competitive advantages. Substantiated claims about fade resistance, weather durability, or extended service life carry more weight than generic statements. Third-party testing certifications based on standardized protocols like JIS K 5600-7-7 for coatings or JIS K 7350-2 for plastics provide additional credibility.
| Weatherometers for Aging Testing | |
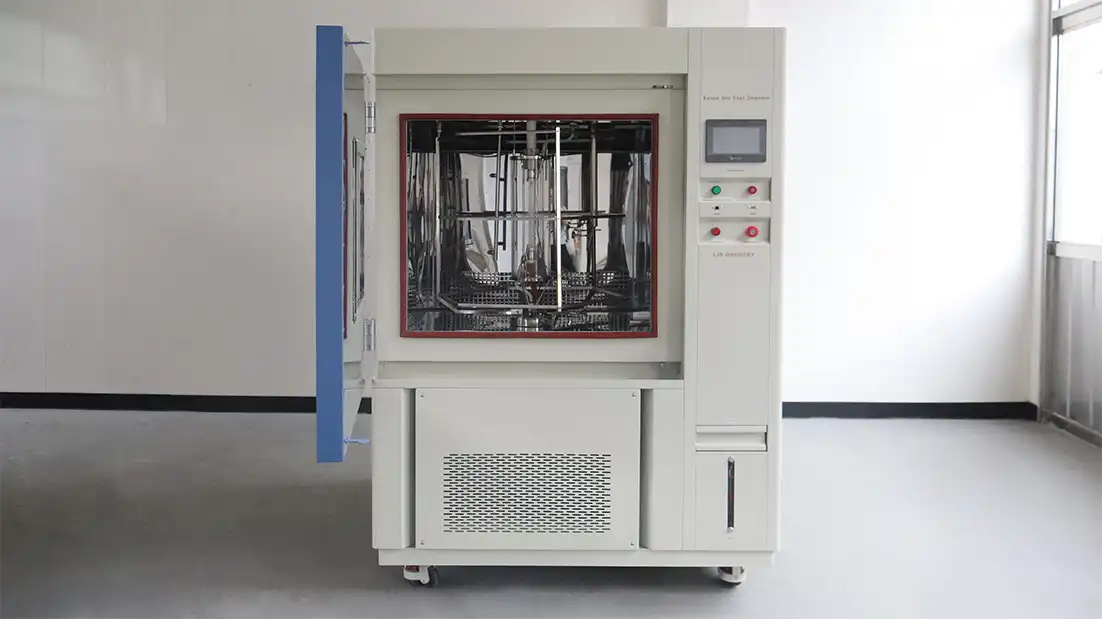 | 1. Advanced Xenon Arc Test Chambers
3. Durable Benchtop High Temperature Chamber
|
Integrating Accelerated Weathering into Product Development Cycles
Strategic placement of weathering evaluation within development workflows maximizes value while minimizing timeline impact.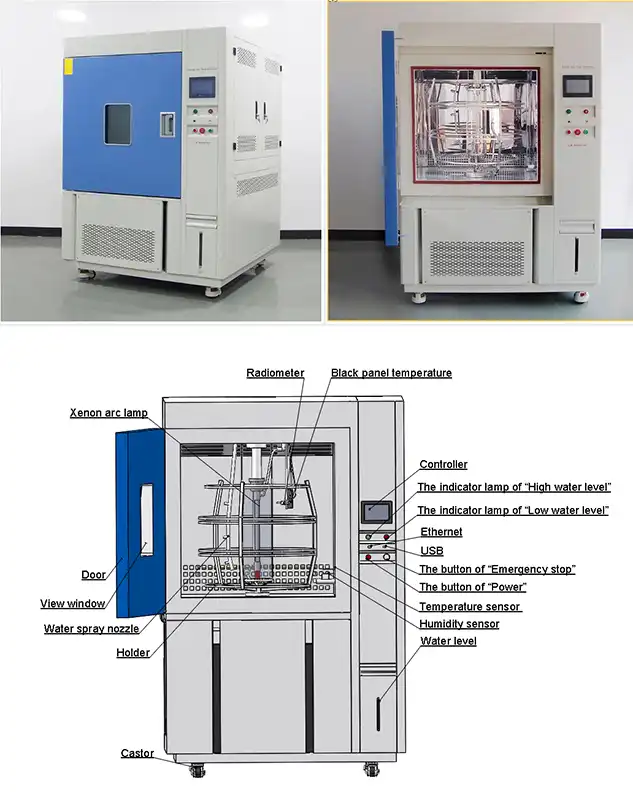
Stage-Gate Testing at Critical Decision Points
Rather than treating weathering as a final validation step, leading organizations incorporate evaluation at multiple development stages. Concept phase screening tests eliminate obviously unsuitable materials, prototype testing validates selected approaches, and pre-production verification confirms manufacturing consistency. This phased approach catches issues early when changes are least expensive.
Parallel Testing to Compress Development Timelines
Simultaneous testing of multiple formulation candidates in separate chamber zones accelerates comparative evaluation. Modern xenon arc weatherometers with programmable controllers and adjustable sample holders accommodate diverse specimen types. This parallelization approach reduces sequential testing delays that extend time-to-market.
Creating Institutional Knowledge Through Test Libraries
Organizations that systematically archive weathering results build valuable reference databases. When developing new products, engineers compare candidate materials against historical performance data from similar applications. This institutional memory prevents repetition of past mistakes and identifies proven material systems for new applications.
Using Test Data to Improve Material Selection and Design Decisions
Weathering information influences choices beyond simple material approval or rejection decisions.
Balancing Performance Trade-offs with Quantitative Data
Materials rarely excel across all performance dimensions simultaneously. Weathering data quantifies specific trade-offs, such as choosing between a formulation offering superior UV resistance but slightly lower impact strength versus an alternative with opposite characteristics. Design teams make informed compromises based on actual service environment priorities.
Optimizing Protective Strategies for Marginal Materials
When cost constraints or other requirements necessitate using materials with limited inherent durability, weathering tests evaluate protective measures. Engineers assess whether UV-absorbing topcoats, sacrificial barrier layers, or design features like drainage channels and ventilation adequately extend service life. Comparative testing with and without protection measures quantifies effectiveness.
Informing Maintenance Schedule Development
For products requiring periodic maintenance, weathering data establishes optimal service intervals. Testing reveals degradation progression rates, identifying when protective treatments need renewal before critical failure thresholds. This information supports maintenance manuals, service contracts, and lifecycle cost projections.
Material Category | Common Applications | Typical Test Duration | Key Failure Indicators |
Automotive coatings | Exterior paint systems | 1000-2000 hours | Gloss retention, color stability |
Architectural fabrics | Awnings, shade structures | 2000-3000 hours | Tensile strength, tear resistance |
Polymer composites | Outdoor furniture, decking | 1500-2500 hours | Surface cracking, dimensional stability |
Electronic assemblies | Solar panels, outdoor displays | 1000-1500 hours | Electrical performance, seal integrity |
Proactively Eliminate Risks with LIB Industry's Reliable Xenon Arc Weatherometer
Implementing comprehensive weathering programs requires dependable testing equipment that delivers consistent, reproducible results over extended operational periods.
Advanced Features Supporting Rigorous Testing Protocols
The XL-S-750C xenon arc weatherometer combines precision environmental control with robust construction for demanding industrial applications. The water-cooled 4500W xenon lamp system with inner quartz and outer borosilicate filters accurately replicates the solar spectrum across critical wavelength ranges. Programmable color LCD touch screen controllers enable complex exposure cycles incorporating light/dark periods, temperature ramps, and moisture spray sequences matching specific climate profiles.

Ensuring Test Accuracy Through Calibrated Monitoring
Integrated UV radiometers with ±5% tolerance continuously monitor irradiance levels, triggering automatic lamp intensity adjustments to maintain consistent exposure throughout test durations. Black panel temperature sensors with ±2°C accuracy verify that specimen surfaces experience intended thermal conditions. Humidity control maintains relative humidity levels between 30% and 98% RH, enabling realistic moisture cycling.
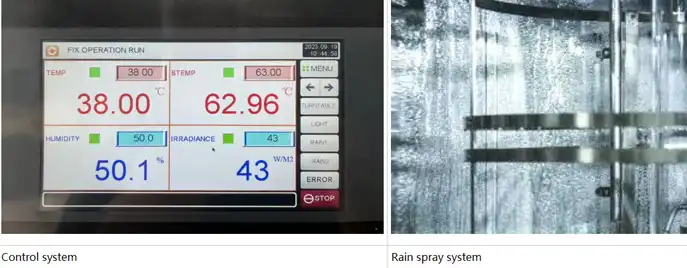
Versatile Application Across Multiple Industries
The 950×950×850mm internal chamber accommodates diverse sample types mounted on rotating holders that ensure uniform exposure. This flexibility serves textile manufacturers validating fabric fade resistance, coating suppliers testing automotive finishes, polymer producers evaluating plastic degradation, and electronics companies assessing outdoor equipment housings. SUS304 stainless steel interior construction with polyurethane foam insulation ensures long-term chamber integrity despite continuous thermal and moisture cycling.
Conclusion
Accelerated weathering testing transforms product development from reactive problem-solving to proactive risk mitigation. By revealing potential failure modes early, correlating laboratory results with field performance, and providing quantitative data for design decisions, xenon arc weatherometers enable manufacturers to deliver more durable products while reducing warranty exposure. Organizations that systematically integrate weathering evaluation throughout development cycles gain competitive advantages through verified performance claims and reduced post-launch quality issues.
FAQ
How long should accelerated weathering tests run to simulate real-world exposure?
Test duration depends on target service life, geographic location, and acceleration factors specific to your material and application. Generally, 1000-2000 hours of xenon arc exposure simulates 1-2 years of outdoor exposure in moderate climates, though correlation studies with field data refine these estimates.
Can xenon arc weatherometers test multiple materials simultaneously?
Modern weathering chambers accommodate multiple specimen types concurrently using adjustable rotating sample holders. This parallel testing capability allows comparative evaluation of different formulations, colors, or protective treatments under identical conditions, accelerating material selection decisions.
What distinguishes xenon arc lamps from other artificial weathering light sources?
Xenon arc lamps produce spectral output closely matching natural sunlight across UV, visible, and infrared wavelengths. This full-spectrum simulation provides more accurate photodegradation assessment compared to fluorescent UV lamps that emphasize narrow UV bands.
Partner with LIB Industry for Superior Environmental Testing Solutions
As a trusted manufacturer and supplier of xenon arc weatherometers, LIB Industry delivers turn-key environmental testing solutions tailored to your validation requirements. Contact ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss how our CE-approved weathering chambers can strengthen your product reliability programs and reduce field failure risks.