In the highly competitive beverage industry, delivering consistent product quality is a top priority. Shelf life test chambers provide accurate hot and cold control to replicate real storage and distribution conditions, from high-temperature warehouse environments to refrigerated supply chains. These controlled settings allow manufacturers to assess key factors such as taste consistency, carbonation stability, microbial activity, and packaging durability—ensuring that every bottle, can, or carton maintains its quality throughout the entire shelf life.
A client from Russia in the instrumentation sector reported strong satisfaction with their experience, stating that their LIB hot and cold chambers has been operating reliably and meeting all performance expectations. This positive feedback highlights the proven stability and performance of LIB chambers in supporting beverage quality testing for customers worldwide.
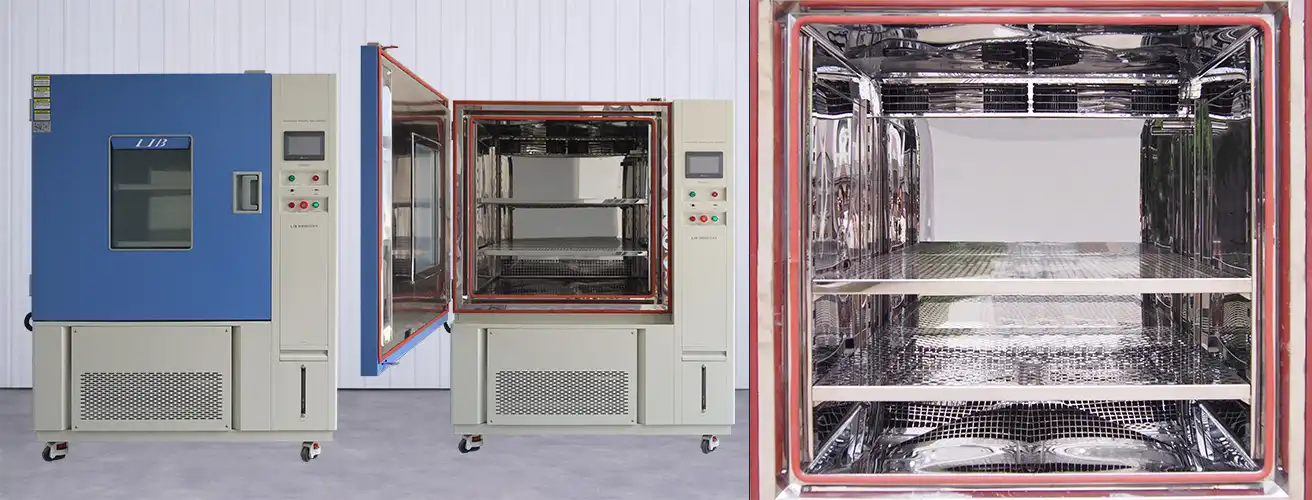
Material stress analysis in hot and cold chambers represents a critical methodology for understanding how materials behave under extreme temperature variations and environmental conditions. These specialized testing environments allow engineers and researchers to simulate real-world stress scenarios, accelerating the evaluation process to predict material performance, durability, and potential failure points. By subjecting samples to controlled temperature cycling between extreme cold and heat, manufacturers can identify weaknesses, optimize material selection, and ensure product reliability before market introduction. This systematic approach has become indispensable across pharmaceutical, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and construction industries, where material integrity directly impacts safety, performance, and regulatory compliance.
Why Material Stress Testing is Essential?
Understanding Material Behavior Under Real Conditions
Materials rarely operate in stable environments. Products face daily temperature fluctuations, seasonal variations, and sudden thermal shocks during transportation and usage. Without comprehensive stress testing, manufacturers risk catastrophic failures, warranty claims, and safety incidents that damage reputation and profitability. Material stress analysis reveals how substances respond to thermal expansion, contraction, and phase transitions that occur during temperature cycling.
Regulatory Compliance and Quality Assurance
Industries operating under strict regulatory frameworks require documented evidence of material performance. Pharmaceutical companies must demonstrate stability according to ICH guidelines, while aerospace manufacturers need certification that components withstand extreme altitude conditions. Hot and cold chamber testing provides the verifiable data necessary for regulatory submissions, quality management systems, and customer specifications.
Cost Reduction Through Early Detection
Identifying material weaknesses during development costs significantly less than addressing field failures. Stress testing uncovers incompatibilities between materials, inadequate bonding in composite structures, and coating failures before production scaling. This proactive approach minimizes redesign expenses, reduces warranty costs, and protects brand integrity by preventing defective products from reaching consumers.

Industry Sector | Testing Priority | Typical Temperature Range |
Pharmaceuticals | Stability validation | -20°C to +40°C |
Electronics | Thermal cycling resistance | -40°C to +85°C |
Automotive | Component durability | -40°C to +150°C |
Simulating Thermal Shock and Environmental Stress
Rapid Temperature Transition Testing
Thermal shock testing involves sudden temperature changes that materials experience during operational transitions. A hot and cold chamber equipped with rapid cooling and heating capabilities can achieve temperature transitions at controlled rates, typically 1°C per minute for cooling and 3°C per minute for heating. This controlled environment replicates scenarios like moving frozen products into ambient conditions or exposing sun-heated components to air conditioning.
Combined Environmental Factor Analysis
Advanced testing protocols combine temperature extremes with humidity variations, creating comprehensive environmental stress profiles. The humidity range of 20% to 98% RH available in modern chambers allows researchers to evaluate moisture absorption, condensation effects, and corrosion acceleration. This multi-factor approach reveals vulnerabilities that single-parameter testing might miss, particularly for materials used in marine, tropical, or variable climate applications.
Cyclic Stress Accumulation Studies
Repeated thermal cycling accumulates stress within materials, eventually leading to fatigue failure. Testing chambers programmed for hundreds or thousands of temperature cycles reveal degradation patterns, crack propagation rates, and life expectancy estimates. These cyclic tests provide critical data for predicting maintenance intervals and establishing product lifespans under specified usage conditions.
| Name | Hot and cold chambers | |||||
Model | TH-100 | |||||
Temperature range | -20℃ ~+150 ℃ | |||||
Low type | A: -40℃ B:-70℃ C -86℃ | |||||
Humidity Range | 20%-98%RH | |||||
Temperature deviation | ± 2.0 ℃ | |||||
Heating rate | 3 ℃ / min | |||||
Cooling rate | 1 ℃ / min | |||||
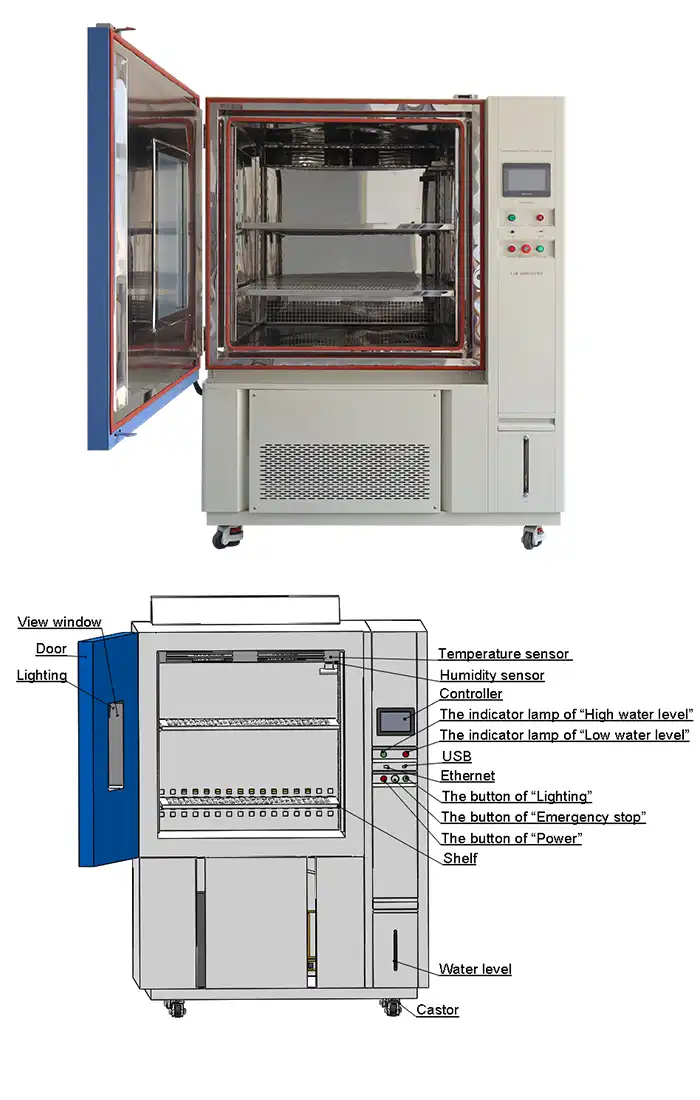
Controller | Programmable color LCD touch screen controller, Multi-language interface, Ethernet , USB | |||||
Exterior material | Steel Plate with protective coating | |||||
Interior material | SUS304 stainless steel | |||||
Standard configuration | 1 Cable hole (Φ 50) with plug; 2 shelves | |||||
Timing Function | 0.1~999.9 (S,M,H) settable | |||||

Evaluating Mechanical Properties under Extreme Conditions
Tensile Strength and Elasticity Changes
Temperature dramatically affects mechanical properties. Polymers become brittle at low temperatures while metals may experience reduced yield strength at elevated temperatures. Testing within a hot and cold chamber allows precise measurement of tensile strength, elongation, and elastic modulus across the operational temperature spectrum, ensuring materials maintain required mechanical properties throughout their service range.
Impact Resistance at Temperature Extremes
Materials that demonstrate adequate toughness at room temperature may become susceptible to brittle fracture when cold or lose structural integrity when hot. Impact testing at controlled temperatures identifies the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature and establishes safety margins for mechanical loading under thermal stress. This data proves essential for components subject to physical impacts during temperature variations.
Dimensional Stability and Thermal Expansion
Different materials exhibit varying coefficients of thermal expansion. When dissimilar materials join in assemblies, temperature changes create internal stresses from differential expansion. Chamber testing measures dimensional changes, warping, and internal stress development, allowing engineers to optimize material pairings and design tolerances that accommodate thermal movement without compromising functionality.
Material Category | Thermal Expansion Coefficient | Critical Testing Range |
Metals (Aluminum) | 23 × 10⁻⁶ /°C | -40°C to +150°C |
Polymers (ABS) | 70-100 × 10⁻⁶ /°C | -20°C to +80°C |
Ceramics | 3-8 × 10⁻⁶ /°C | -70°C to +150°C |
Identifying Material Weak Points and Failure Modes
Interface Degradation in Composite Materials
Composite materials rely on strong bonding between constituents. Temperature cycling stresses these interfaces, potentially causing delamination, debonding, or void formation. Hot and cold chamber analysis with periodic inspection identifies interface weaknesses, allowing formulation adjustments or processing modifications to enhance bonding durability before production commitments.
Coating and Surface Treatment Evaluation
Protective coatings, paints, and surface treatments must maintain adhesion and integrity across temperature ranges. Thermal stress testing reveals coating failures including cracking, blistering, peeling, or discoloration that compromise protection or aesthetics. This evaluation guides coating selection and application parameters to ensure long-term surface protection.
Crystallization and Phase Change Detection
Some materials undergo phase transitions at specific temperatures, affecting their properties dramatically. Polymers may crystallize, oils can solidify, and certain alloys form undesirable phases when thermally cycled. Chamber testing with analytical techniques detects these changes, enabling formulation optimization or establishing temperature limits for safe operation.
Accelerated Testing for Product Longevity
Lifetime Prediction Modeling
Accelerated thermal cycling compresses years of natural aging into weeks or months of testing. By applying more severe conditions than anticipated in service, researchers establish degradation rates and extrapolate to predict product lifespans. This modeling relies on chamber testing data combined with statistical analysis to provide confidence intervals for warranty periods and replacement recommendations.
Arrhenius-Based Degradation Studies
Chemical reaction rates typically double with every 10°C temperature increase. Hot and cold chamber testing at elevated temperatures accelerates degradation mechanisms, allowing application of Arrhenius equations to predict performance at lower temperatures over extended periods. This approach proves particularly valuable for pharmaceutical stability testing and electronic component reliability assessment.
Comparative Material Screening
When evaluating multiple material candidates, accelerated testing quickly differentiates superior performers from inadequate options. Simultaneous testing of variants within a hot and cold chamber with consistent protocols eliminates environmental variables, providing reliable comparative data for material selection decisions that impact cost, performance, and sustainability.
Test Duration | Equivalent Field Exposure | Testing Conditions |
1 week | 3-6 months | Continuous cycling, -40°C to +80°C |
4 weeks | 1-2 years | Daily cycles with humidity variation |
12 weeks | 3-5 years | Comprehensive protocol with hold periods |
Reveal Material Limits with LIB Industry's Advanced Hot and Cold Chamber
Precision Control for Accurate Results
LIB Industry hot and cold chambers feature programmable color LCD touch screen controllers with Ethernet connectivity, enabling precise temperature and humidity programming. Temperature fluctuation maintained within ±0.5°C and deviation within ±2.0°C ensures consistent conditions across test durations. This precision eliminates environmental variables that could confound results, providing confidence in material performance assessments.
Versatile Configuration Options
Available in multiple sizes from 100L to 1000L interior volumes, LIB chambers accommodate diverse sample sizes and testing requirements. Temperature range options extending from -70°C to +150°C cover virtually all material testing needs across industries. The modular design allows customization for specific applications, including integration with vibration systems, corrosion testing capabilities, or altitude simulation.
Comprehensive Safety and Reliability Features
Built-in protection systems including humidifier dry-combustion protection, over-temperature safeguards, refrigerant high-pressure protection, and earth leakage protection ensure operator safety and equipment longevity. The French TECUMSEH compressor delivers reliable refrigeration, while stainless steel construction resists corrosion from humidity and temperature extremes. These features provide consistent performance for demanding testing schedules.
Turn-Key Testing Solutions
LIB Industry provides complete support from initial consultation through installation and training. This comprehensive approach ensures chambers integrate seamlessly into existing quality systems, operators receive proper training for accurate testing, and ongoing technical support maintains optimal performance. The three-year warranty demonstrates confidence in equipment reliability and manufacturer commitment to customer success.
Data Management and Documentation
Ethernet connectivity enables real-time monitoring, automated data logging, and integration with laboratory information management systems. This capability streamlines compliance documentation, facilitates trend analysis across multiple test runs, and supports statistical process control initiatives. Digital records eliminate transcription errors and provide audit trails required for regulatory submissions.
Applications Across Industries
Pharmaceutical companies utilize these chambers for ICH-compliant stability studies of active ingredients and formulations. Electronics manufacturers evaluate solder joint reliability and component tolerance. Automotive suppliers test seal materials, lubricants, and interior components. Research institutions conduct fundamental material science investigations. This versatility makes LIB chambers valuable across diverse sectors requiring material stress analysis.
Conclusion
Material stress analysis conducted in hot and cold chambers provides essential insights into product reliability, safety, and performance under real-world conditions. Through systematic evaluation of thermal shock resistance, mechanical property variations, and accelerated aging, manufacturers optimize material selection and design parameters before market introduction. LIB Industry's advanced chambers deliver the precision, versatility, and reliability necessary for comprehensive material characterization across pharmaceutical, industrial, and research applications.
FAQs
What temperature cycling rate is appropriate for material stress testing?
Cycling rates depend on application requirements and material thermal mass. Rapid cycles (1-3°C per minute) simulate thermal shock, while slower transitions assess gradual environmental changes. LIB chambers offer programmable rates allowing customization for specific testing protocols and material sensitivities.
How does humidity control enhance material stress analysis?
Humidity interacts with temperature to affect moisture absorption, dimensional changes, and corrosion rates. Combined temperature-humidity testing reveals vulnerabilities in hygroscopic materials, evaluates barrier properties, and simulates tropical or marine environments more accurately than temperature testing alone.
What sample size considerations affect chamber selection?
Chamber selection should accommodate sample dimensions with adequate air circulation space, typically requiring 30-40% of chamber volume remain unoccupied. Multiple samples tested simultaneously require uniform temperature distribution, making larger chambers with advanced air circulation systems preferable for comprehensive material screening programs.
Partner with LIB Industry for Your Material Testing Needs
As a leading hot and cold chamber manufacturer and supplier, LIB Industry delivers turn-key environmental testing solutions tailored to your requirements. Contact us at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss your material stress analysis needs and discover how our chambers enhance your quality assurance programs.