MIL-STD-810G Rain Test Chambers for Military Equipment Testing
Military equipment operates in the harshest environments imaginable, where exposure to rain and moisture can compromise mission-critical systems. MIL STD 810 G rain test chambers provide the controlled testing infrastructure necessary to validate equipment durability against water ingress. These specialized chambers simulate various precipitation conditions - from light drizzle to driving rainstorms - enabling defense contractors and military organizations to verify that electronics, communication systems, vehicles, and protective gear meet rigorous military specifications before deployment. Understanding how these chambers work and their role in equipment qualification helps manufacturers deliver reliable solutions that protect warfighters in adverse conditions.
Why Rain Resistance Is Critical for Military Equipment?
Operational Environment Challenges

Military operations rarely occur in favorable weather conditions. Combat zones span tropical rainforests, monsoon-affected regions, and maritime environments where equipment faces continuous moisture exposure. Electronic components, optical systems, and mechanical assemblies must maintain functionality despite water intrusion attempts. A single compromised seal or inadequate coating can render communication devices inoperative, navigation systems unreliable, or weapon platforms ineffective during critical operations.
Consequences of Water Ingress Failures
Equipment failures during deployment carry severe consequences beyond mission compromise. Water penetration causes short circuits in electronic assemblies, corrosion in metal components, and degradation of protective coatings. These failures endanger personnel who depend on reliable equipment for situational awareness, communication, and protection. The financial impact of field failures includes emergency replacement costs, logistics challenges, and potential loss of multi-million-dollar platforms.
Validation Before Deployment
Proactive testing identifies design weaknesses before equipment reaches the battlefield. Manufacturers utilize controlled chamber environments to expose prototypes to water ingress scenarios that mirror years of field exposure. This validation process reveals seal inadequacies, coating deficiencies, and drainage system flaws that require correction. Early detection during development reduces costly redesigns and prevents catastrophic failures during operational use.
Overview of MIL-STD-810G Rain Test Requirements
Standard Framework and Procedures
MIL-STD-810H (the current revision of the 810G standard) establishes three distinct test procedures addressing different precipitation scenarios. Procedure I evaluates resistance to wind-driven rain with droplets impacting surfaces at realistic velocities up to 9 meters per second. Procedure II generates exaggerated rainfall conditions exceeding natural storm intensity, validating equipment against extreme weather events. Procedure III simulates drip conditions for equipment installed under protective structures where water accumulation and drainage become primary concerns.
Equipment Classification Requirements
Different equipment categories face varying exposure levels based on deployment scenarios. Portable field equipment requires testing under Procedure I conditions since soldiers carry these items through driving rainstorms. Vehicle-mounted systems undergo Procedure II evaluation, as vehicular motion through precipitation creates intensified water impact conditions. Shelter-housed equipment qualifies under Procedure III, where roof leaks and condensation pose greater threats than direct rainfall exposure.
Compliance Documentation Standards
Successful blowing rain test chamber testing generates detailed documentation demonstrating compliance with military specifications. Test reports include environmental parameters, specimen orientation records, exposure duration data, and post-test inspection results. This documentation supports contract requirements, quality system audits, and certification processes. CNAS/ILAC traceable calibration certificates verify chamber accuracy, ensuring test validity and regulatory acceptance across international defense markets.
Test Procedure | Primary Application | Wind Speed | Rainfall Rate |
Procedure I | Portable equipment, exposed installations | Up to 18 m/s | ≥ 1.7 mm/min |
Procedure II | Vehicle systems, aircraft components | Minimal | 20.8 L/min |
Procedure III | Sheltered equipment, fixed installations | None | 280 L/m²/h |
Test Parameters: Water Pressure, Spray Angle, and Duration
Droplet Size and Velocity Control
Natural rainfall exhibits specific droplet characteristics that chambers must replicate accurately. The MIL STD 810 G rain test chamber generates droplets ranging from 0.5mm to 4.5mm diameter, matching the size distribution observed in actual rainstorms. Terminal velocity achievement ensures droplets impact test specimens at 9 meters per second, duplicating the kinetic energy of natural precipitation. This velocity specification proves critical since water penetration through seals and gaskets depends heavily on impact force rather than mere contact.
Water Temperature Differential Management
Temperature relationships between water and test specimens significantly influence condensation formation and thermal shock effects. Chamber systems maintain water temperatures at specimen temperature plus 10°C, with maximum water temperatures reaching 55°C for tropical environment simulation. This differential creates realistic conditions where warm equipment meets cooler rainfall, generating condensation patterns that reveal design vulnerabilities. Temperature control also prevents unrealistic thermal gradients that might mask actual field performance issues.
Exposure Duration and Cycle Programming
Test duration selection balances accelerated testing principles with realistic exposure modeling. Standard test cycles range from continuous exposure periods up to 999 minutes, programmable through the chamber's human-machine interface. Extended duration testing reveals time-dependent failure mechanisms including seal degradation, coating breakdown, and progressive water intrusion. Cycle programming accommodates intermittent exposure scenarios where equipment experiences repeated wetting and drying cycles common in operational environments.
| ||
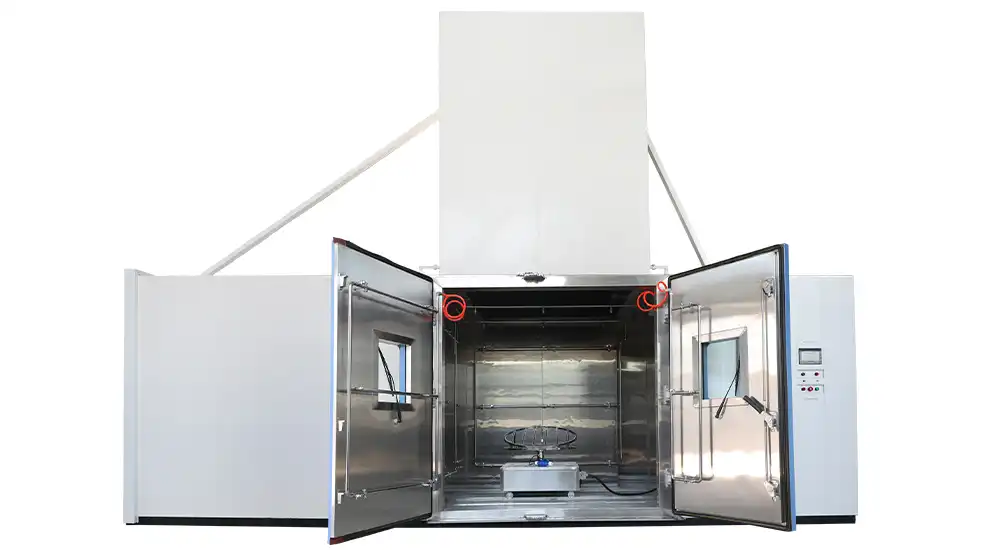
Model: RIM-1000 | Interior Volume: 1000 L Turntable Load: 50 kg Turntable Diameter: 800 mm Door Lock: Electromagnetic lock Interior Material: SUS304 stainless steel Test Standard: MIL-STD-810H Test Time: 0 – 999 min, adjustable |
|
Rain & Blowing Rain | Final Rain Droplet Velocity: 9 m/s on test item Rainfall Rate ≥ 1.7 mm/min | |
Droplet Size: 0.5 – 4.5 mm Water Temperature: +10°C to max. +55°C | ||
Exaggerated Rain | Nozzle Pressure: 276 kPa Rainfall Rate: 20.8 L/min Nozzle Arrangement: One nozzle per 0.56 m² of surface area, approx. 48 cm from test surface Droplet Size:0.5 – 4.5 mm | |
Drip | Drip Area Dimensions: 1600 × 1000 mm, height adjustable Drip Hole Diameter: 20 – 25.4 mm Distance Between Holes: 25 mm Water Volume: ≥ 280 L/m²/h Water Temperature: +10°C to max. +55°C | |
Simulating Field Rain Conditions Using Test Chambers
Nozzle Array Configuration
Specialized nozzle arrangements ensure uniform water distribution across test specimen surfaces. The chamber employs one nozzle per 0.56 square meters of test surface area, positioned approximately 48 centimeters from specimens. This spacing prevents localized water concentration while ensuring complete coverage. Nozzle pressure calibration at 276 kilopascals generates proper droplet atomization and spray patterns matching standard requirements. Multiple nozzle types accommodate different test procedures from fine mist generation to concentrated stream delivery.
Wind Generation Systems
High-powered blower frameworks produce wind speeds reaching 18 meters per second, replicating storm conditions where horizontal rain components challenge protective designs. Variable speed control allows precise wind velocity adjustment matching specific test requirements. The airflow combines with water spray to create wind-driven rain at controlled angles relative to specimen orientation. This capability proves essential since most water intrusion occurs through vertical surfaces during storm events rather than top-mounted openings.
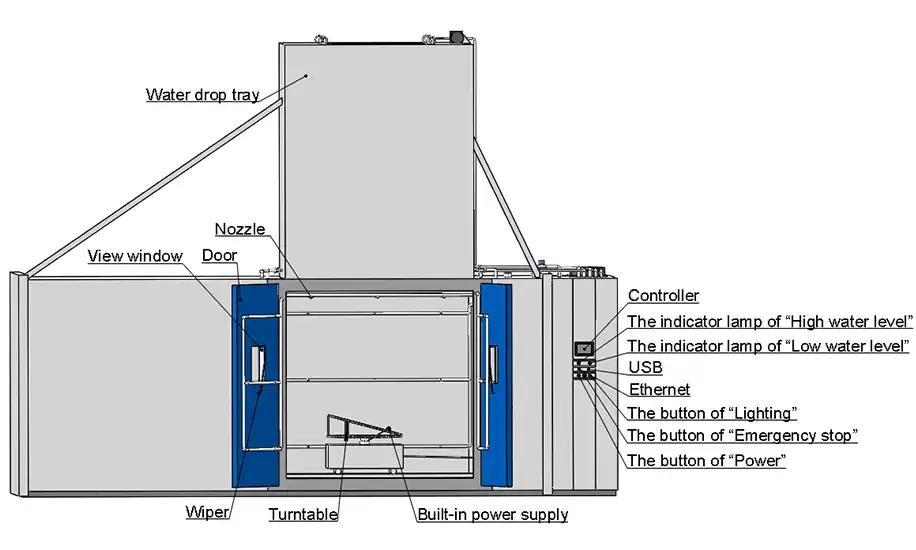
Turntable Rotation and Specimen Positioning
A precision rotating turntable with 50-kilogram load capacity enables 360-degree specimen exposure. Rotation speeds between 1-7 revolutions per minute ensure all equipment surfaces face simulated weather conditions throughout the test cycle. The 800mm diameter platform accommodates various equipment sizes while maintaining balance and stability. Adjustable specimen mounting fixtures secure items at proper angles, simulating actual installation orientations. This comprehensive exposure capability reveals vulnerabilities that fixed-position testing might miss.
Chamber Component | Specification | Function |
Nozzle Pressure | 276 kPa | Droplet atomization control |
Turntable Capacity | 50 kg | Specimen rotation for complete exposure |
Wind Speed Range | 0-18 m/s | Wind-driven rain simulation |
Chamber Volume | 1000 L | Adequate test space for military equipment |
Analyzing Equipment Performance After Rain Exposure
Water Penetration Detection Methods
Post-test inspection employs multiple detection techniques revealing water intrusion evidence following exposure in a MIL STD 810 G rain test chamber. Visual examination identifies obvious water accumulation, corrosion initiation, and coating damage. Electrical continuity testing detects moisture presence in electronic assemblies through insulation resistance measurements. Indicator papers placed inside sealed enclosures reveal even minimal water penetration through color changes. Functional testing under operational parameters verifies that equipment maintains performance specifications despite moisture exposure.
Seal Integrity Evaluation
Gasket and seal performance represents the primary defense against water ingress. Inspection protocols examine seal compression, material degradation, and contact surface conditions. Pressure decay testing quantifies seal effectiveness by measuring enclosure pressurization loss rates. Disassembly reveals whether seals maintained proper compression throughout testing or exhibited permanent deformation. This evaluation identifies design improvements including material selection changes, compression optimization, or seal geometry modifications.
Corrosion Assessment Procedures
Accelerated corrosion resulting from water exposure indicates coating inadequacies or material incompatibilities. Metallurgical examination documents corrosion type, location, and severity using standardized rating scales. Surface preparation analysis determines whether coating adhesion failures contributed to corrosion initiation. Electrochemical testing measures corrosion potential and polarization resistance, predicting long-term material performance. These assessments guide protective coating improvements and material substitutions enhancing equipment durability.
Enhancing Military Equipment Reliability Through Rain Testing
Design Iteration and Improvement Cycles
Chamber testing results drive systematic design refinements throughout development programs. Initial prototype testing reveals fundamental design flaws requiring significant modifications. Subsequent iterations incorporate seal improvements, drainage enhancements, and coating upgrades. Validation testing confirms modification effectiveness before production commitment. This iterative approach compresses the development timeline by identifying issues early rather than discovering problems during field trials or operational deployment.
Material Selection Optimization
Water resistance depends heavily on proper material selection for seals, gaskets, coatings, and structural components. Testing exposes material performance under realistic environmental stress, revealing elastomer swelling, coating delamination, or metal corrosion susceptibility. Comparative testing of alternative materials identifies optimal solutions balancing performance, cost, and availability. Material qualification testing under standard conditions enables objective selection decisions supported by documented performance data rather than theoretical predictions.
Manufacturing Quality Verification
Production equipment requires periodic testing verifying manufacturing consistency and quality control effectiveness. Sample testing from production lots confirms that assembly processes maintain seal integrity, coating application quality, and drainage system functionality. Statistical sampling plans balance testing costs against confidence requirements. Failure trends identified during production testing trigger process investigations preventing widespread quality escapes. This ongoing verification maintains reliability standards throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Ensure Strict Military Compliance with LIB Industry MIL STD 810 G Rain Test Chambers
Advanced Multi-Procedure Capability
LIB Industry blowing rain test chambers support all three MIL-STD-810H procedures within a single integrated platform. This versatility eliminates the need for multiple specialized chambers, reducing capital investment and laboratory space requirements. Automated procedure switching through the programmable control system streamlines testing workflows. Operators configure test parameters through the intuitive HMI, selecting rainfall rates, wind speeds, water temperatures, and exposure durations matching specific procedure requirements. The system automatically activates appropriate nozzle arrays, wind generation, and heating elements.
Precision Control and Monitoring Systems
Integrated flow meters and rain gauges provide closed-loop feedback maintaining accurate rainfall rates throughout testing. Water temperature control systems preserve the required thermal differential between water and specimens. Real-time monitoring displays current conditions, alerts operators to parameter deviations, and records data for comprehensive test reports. The electromagnetic door lock system prevents accidental access during testing while maintaining chamber integrity. Multi-layer sealing prevents laboratory flooding through robust door seals and rapid drainage systems.
Global Support Infrastructure
Since 2009, LIB Industry has established partnerships with world-renowned organizations including Apple, IBM, Amazon, Intel, SGS, TUV, and Mercedes-Benz. The network of 29 global agents and service centers across Malaysia, Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States provides localized technical support. Rapid response times minimize downtime, while expert assistance ensures optimal chamber performance. Complete documentation packages include CNAS/ILAC traceable calibration certificates supporting quality system requirements and facilitating audit processes.
Feature Category | Capability | Benefit |
Test Procedures | I, II, and III support | Complete standard compliance |
Internal Dimensions | 1000×1000×1000 mm | Accommodates diverse equipment |
Control System | Programmable HMI with data logging | Automated testing and documentation |
Global Support | 29 agents and service centers | Rapid response and expert assistance |
Conclusion
MIL STD 810 G rain test chambers represent essential infrastructure for validating military equipment durability against water ingress threats. These sophisticated systems simulate realistic precipitation conditions revealing design vulnerabilities before operational deployment. Through comprehensive testing across multiple procedures, manufacturers demonstrate equipment compliance with rigorous military specifications protecting personnel and ensuring mission success. Investment in proper testing infrastructure reduces field failures, extends equipment service life, and maintains warfighter confidence in their critical systems.
FAQ
What distinguishes MIL-STD-810G rain testing from commercial IP rating tests?
MIL-STD-810G evaluates equipment under dynamic environmental conditions including wind-driven rain, temperature differentials, and extended exposure durations mirroring actual military operational scenarios. Commercial IP ratings test static water intrusion resistance without environmental complexity, making them insufficient for military qualification requiring comprehensive environmental exposure validation under realistic deployment conditions.
How frequently should military equipment undergo rain chamber testing during development?
Rain testing occurs at multiple development stages beginning with initial prototype evaluation, continuing through design iteration validation, and concluding with production qualification testing. Critical design modifications trigger additional testing cycles. Production equipment undergoes periodic sampling verification ensuring manufacturing consistency. This multi-phase approach identifies issues early while confirming reliability throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Can existing equipment be retrofitted and tested for improved rain resistance?
Existing equipment benefits from chamber testing identifying specific water intrusion paths requiring remediation. Retrofit solutions include enhanced sealing systems, protective coating applications, drainage improvements, and component enclosure modifications. Post-retrofit testing validates improvement effectiveness ensuring upgraded equipment meets military specifications. This approach extends equipment service life while enhancing operational reliability.
LIB Industry, as a leading environmental test chamber manufacturer and supplier, delivers turn-key solutions supporting military equipment qualification programs worldwide. Our MIL STD 810 G rain test chambers combine advanced technology, precision control, and comprehensive support infrastructure. Contact our team at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss your specific testing requirements and discover how our chambers enhance your equipment reliability validation processes.