Shelf Life Test Chamber Applications in Sterile Packaging Validation
In the highly competitive beverage industry, ensuring consistent product quality is critical. Shelf life test chambers provide precise control over temperature and humidity, replicating real-world storage environments—from sweltering warehouses to chilled transport systems. These chambers allow manufacturers to assess flavor stability, carbonation retention, microbial growth, and packaging integrity, guaranteeing that every bottle, can, or carton maintains its intended quality throughout its shelf life.
A satisfied Russian client in the instrumentation sector commented: “Our LIB temperature-humidity chamber has been operating flawlessly. Everything works perfectly, and the chamber meets all our expectations.” Feedback like this highlights the reliability and performance of LIB chambers in supporting beverage quality assurance for customers worldwide.
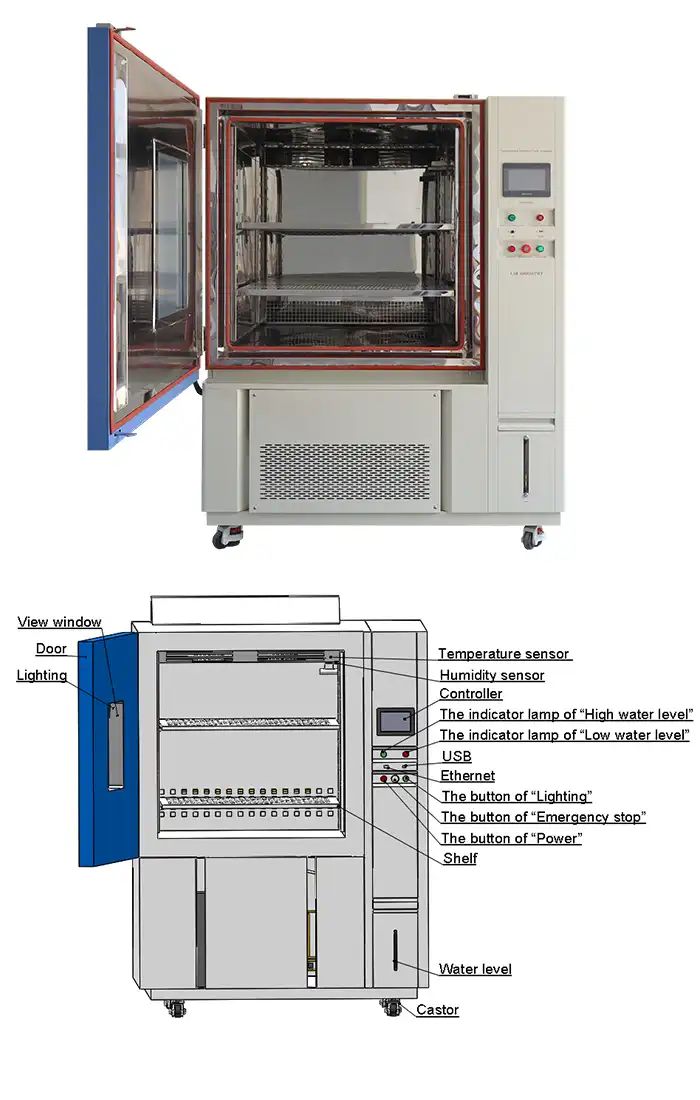
Sterile packaging validation relies on shelf life test chambers to ensure medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and food products maintain their sterility throughout their intended lifespan. These environmental simulation systems replicate extreme temperature fluctuations, humidity variations, and prolonged storage conditions that challenge package integrity. By subjecting sterile barriers to accelerated aging protocols within controlled chambers, manufacturers verify seal strength, material compatibility, and microbial ingress prevention before market release. The validation process combines thermal cycling, ambient stress exposure, and real-time monitoring to predict package performance across distribution chains and storage facilities worldwide.
Importance of Sterile Packaging Validation
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Medical device manufacturers must demonstrate package sterility maintenance per ISO 11607 standards, which mandate documented evidence of barrier system effectiveness. Regulatory bodies including FDA, EMA, and Health Canada require validation data proving sterile products withstand transportation stresses and shelf storage without compromising patient safety. Testing protocols must address temperature extremes ranging from -86°C to +150°C, simulating global distribution scenarios from arctic shipping routes to tropical warehouse conditions.
evidence of barrier system effectiveness. Regulatory bodies including FDA, EMA, and Health Canada require validation data proving sterile products withstand transportation stresses and shelf storage without compromising patient safety. Testing protocols must address temperature extremes ranging from -86°C to +150°C, simulating global distribution scenarios from arctic shipping routes to tropical warehouse conditions.
Patient Safety and Product Efficacy
Compromised sterile barriers expose patients to infection risks that can lead to surgical complications, device malfunction, or therapeutic failures. A single breach in packaging integrity allows bacterial contamination within minutes, rendering life-saving implants or injectable medications hazardous. Validation testing identifies weak points in tray designs, seal configurations, and material selections before products reach clinical settings, protecting vulnerable patient populations.
Economic Impact of Validation Failures
Product recalls due to sterility breaches cost manufacturers millions in lost inventory, regulatory penalties, and brand reputation damage. A comprehensive validation program using environmental test chambers reduces market entry delays by 30-40% compared to reactive testing approaches. Early detection of packaging vulnerabilities during development phases prevents costly post-market surveillance findings and maintains competitive advantages in regulated markets.
How Environmental Stress Tests Affect Sterility?
Temperature Cycling Effects on Seal Integrity
Repeated thermal expansion and contraction cycles stress heat-sealed joints, creating microscopic channels for microbial penetration. The TH-225 shelf life test chamber's temperature range capability from -86°C to +150°C enables simulation of freeze-thaw cycles experienced during air cargo transport and ground delivery. Testing reveals whether adhesive bonds weaken, polymer substrates become brittle, or Tyvek-to-foil interfaces separate under thermal stress, each representing potential sterility failure modes.
Humidity Impact on Barrier Materials
Moisture ingress through porous substrates or seal imperfections compromises sterile environments by creating pathways for bacterial migration. Chambers maintaining 20%-98% RH ranges expose packages to condensation formation, material swelling, and adhesive degradation that occur during seasonal humidity shifts. Paper-based medical packaging shows particular vulnerability to dimensional changes above 70% RH, while polymer films may lose electrostatic barriers that repel particulate contamination.
Accelerated Aging Kinetics
Elevated temperature exposure accelerates chemical degradation reactions following Arrhenius principles, where every 10°C increase doubles reaction rates. Real-time aging requiring three years at 25°C ambient conditions compresses into 6-12 months at 55°C accelerated testing, providing rapid validation data. The programmable LCD touchscreen controller enables precise thermal profiles that correlate accelerated results with shelf life predictions through established mathematical models.
Environmental Parameter | Testing Range | Sterility Impact |
Temperature Extremes | -86°C to +150°C | Seal stress, material brittleness |
Humidity Variation | 20% - 98% RH | Moisture ingress, adhesive failure |
Thermal Cycling | ±0.5°C precision | Fatigue cracking, delamination |
Monitoring Integrity of Barrier Packaging
Dye Penetration Testing Protocols
Sterile barrier validation employs colored dye solutions applied to package exteriors before chamber exposure, revealing microscopic breaches through interior staining patterns. Post-aging inspection under controlled lighting conditions identifies seal defects measuring 50-100 micrometers, below visual detection thresholds. The mirror-surface stainless steel interior of the TH-225 facilitates contamination-free testing environments, preventing false positives from chamber-introduced particulates.
breaches through interior staining patterns. Post-aging inspection under controlled lighting conditions identifies seal defects measuring 50-100 micrometers, below visual detection thresholds. The mirror-surface stainless steel interior of the TH-225 facilitates contamination-free testing environments, preventing false positives from chamber-introduced particulates.
Microbial Challenge Studies
Aerosolized bacterial spores applied to aged packages quantify actual microbial barrier performance rather than physical defect measurements alone. Shelf life test chambers maintaining stable temperature deviation of ±2.0°C throughout testing periods ensure consistent challenge conditions across multiple validation batches. Recovery rates below 10⁻⁶ probability levels satisfy regulatory sterility assurance requirements, demonstrating package integrity under worst-case environmental exposure scenarios.
Physical Testing Methodologies
Burst strength, peel force, and tensile testing conducted on environmentally aged samples reveal mechanical property changes affecting sterile barrier maintenance. Packages exposed to 3°C/min heating rates and 1°C/min cooling rates within chambers experience representative thermal stress gradients matching distribution realities. Quantitative measurements track degradation curves, establishing acceptance criteria for material specifications and process controls.
Accelerated Shelf Life Testing for Sterile Products
Establishing Equivalency Factors
Validation scientists calculate aging equivalency factors (AEF) relating accelerated temperature exposure to real-time ambient aging through activation energy determinations. Medical device standards recommend 55°C as the accelerated test temperature, providing 10× time compression versus 25°C room temperature storage. The R404A and R23 environmentally friendly refrigerant systems enable precise temperature control across the full range needed for both accelerated protocols and worst-case cold storage simulations.
Multi-Factor Stress Testing
Combined temperature-humidity stress testing reveals synergistic degradation mechanisms invisible in single-parameter studies. Packages stable at elevated dry heat may fail catastrophically under humid heat conditions where hydrolysis reactions accelerate. The forced air convection system ensures uniform environmental distribution throughout the 500×600×750mm internal chamber dimension, eliminating hot spots that invalidate test results through non-uniform aging.
Validation Timeline Optimization
Strategic use of accelerated testing reduces product development cycles from 5-7 years to 18-24 months while maintaining scientific rigor. Real-time confirmatory studies run parallel to accelerated protocols, providing verification data as products enter distribution. Programmable controllers with Ethernet and USB connectivity facilitate automated data collection across extended validation periods, reducing labor costs and improving documentation quality.
Aging Protocol | Temperature | Duration | Real-Time Equivalent |
Real-Time | 25°C | 36 months | 36 months |
Accelerated | 55°C | 3.6 months | 36 months |
Extreme Accelerated | 70°C | 1 month | 12 months |
Predicting Shelf Life under Sterile Conditions
Arrhenius Modeling Applications
Mathematical models correlating temperature exposure with degradation rates enable extrapolation from accelerated test data to claimed shelf life periods. Activation energy calculations derived from multi-temperature studies provide confidence intervals for expiration date assignments. The high-precision PT100Ω temperature probe ensures measurement accuracy within ±0.1°C, critical for generating reliable Arrhenius plots supporting regulatory submissions.
Package Design Optimization
Shelf life predictions identify materials and configurations maximizing sterility assurance across target distribution environments. Comparative testing of competing barrier films, adhesive systems, and sterilization-compatible substrates guides material selection decisions worth millions in procurement costs. Shelf life test chamber customization capabilities including explosion-proof modifications enable testing of ethylene oxide or gamma radiation sterilized products without cross-contamination risks.
Distribution Chain Mapping
Temperature and humidity data loggers placed throughout global distribution networks provide environmental profiles for validation protocol development. Chamber programming replicates documented field exposures, from equatorial port delays to refrigerated pharmaceutical logistics. Network port remote control capabilities allow validation teams to adjust protocols based on emerging distribution data without interrupting ongoing studies.
Distribution Environment | Temperature Range | Humidity Range | Typical Duration |
Tropical Warehousing | 30-40°C | 70-95% RH | 12-24 months |
Refrigerated Shipping | 2-8°C | 40-60% RH | 2-7 days |
Arctic Transportation | -40 to -20°C | 10-30% RH | 3-14 days |
Validate Sterile Packaging with LIB Industry's Advanced Shelf Life Test Chamber
Technical Specifications for Validation Success
The TH-225 and TH-500 models provide internal dimensions accommodating full production-scale package formats, eliminating concerns about sample size representativeness. Programmable color LCD touchscreen controllers with multi-language interfaces simplify protocol execution across international validation teams. The punch-designed sample shelves facilitate drainage during condensing humidity tests, preventing water accumulation that could compromise test integrity.
| Name | shelf life test chamber | |||||
Model | TH-100 | |||||
Temperature range | -20℃ ~+150 ℃ | |||||
Low type | A: -40℃ B:-70℃ C -86℃ | |||||
Humidity Range | 20%-98%RH | |||||
Temperature deviation | ± 2.0 ℃ | |||||
Heating rate | 3 ℃ / min | |||||
Cooling rate | 1 ℃ / min | |||||
Controller | Programmable color LCD touch screen controller, Multi-language interface, Ethernet , USB | |||||
Exterior material | Steel Plate with protective coating | |||||
Interior material | SUS304 stainless steel | |||||
Standard configuration | 1 Cable hole (Φ 50) with plug; 2 shelves | |||||
Timing Function | 0.1~999.9 (S,M,H) settable | |||||
Quality System Integration
Independent water systems and electrical systems enhance operational safety during unattended overnight and weekend testing runs essential for accelerated protocols. USB port data download capabilities integrate chamber recordings directly into electronic quality management systems, supporting 21 CFR Part 11 compliance for paperless validation documentation. The mirror-surface stainless steel interior minimizes cleaning time between test cycles, preventing cross-contamination between product families.
Global Manufacturer Support
LIB Environmental Simulation Industry concentrates on providing turn-key solutions for environmental testing, encompassing research, design, production, commissioning, delivery, installation, and training. The company's customization capabilities address unique validation requirements including low-pressure altitude simulation, vibration combined environmental testing, and explosion-proof construction for volatile sterilant exposure studies. CE-approved manufacturing standards ensure equipment compatibility with international laboratory accreditation requirements.
Conclusion
Shelf life test chambers serve as indispensable validation tools for sterile packaging systems, transforming months-long aging studies into accelerated protocols while maintaining scientific accuracy. Environmental stress testing identifies material vulnerabilities, predicts long-term performance, and supports regulatory submissions across pharmaceutical, medical device, and sterile food industries. Investment in advanced chamber technology reduces development costs, accelerates market entry, and protects patient safety through comprehensive barrier integrity validation.
FAQs
What temperature range is required for comprehensive sterile packaging validation?
Validation protocols should encompass -40°C to +60°C representing global distribution extremes, with accelerated aging typically conducted at 55°C. Medical device standards may require testing down to -86°C for products experiencing ultra-cold chain logistics or cryogenic sterilization processes.
How long does accelerated shelf life testing take for sterile medical devices?
Accelerated protocols at 55°C typically require 3-6 months to simulate 3-year shelf life claims, depending on activation energy values and regulatory requirements. Real-time confirmatory studies run parallel, providing verification data spanning the full claimed expiration period.
Can shelf life test chambers simulate both temperature and humidity stress simultaneously?
Modern chambers maintain precise temperature and humidity control concurrently, enabling worst-case tropical condition simulation at 40°C/90% RH or other combined environmental profiles. This capability reveals synergistic degradation mechanisms invisible in single-parameter testing approaches.
Contact LIB Industry Today
As a leading manufacturer and supplier of shelf life test chambers, LIB Industry delivers factory-direct pricing on CE-approved equipment available in stock. Request your quotation at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss customized validation solutions.