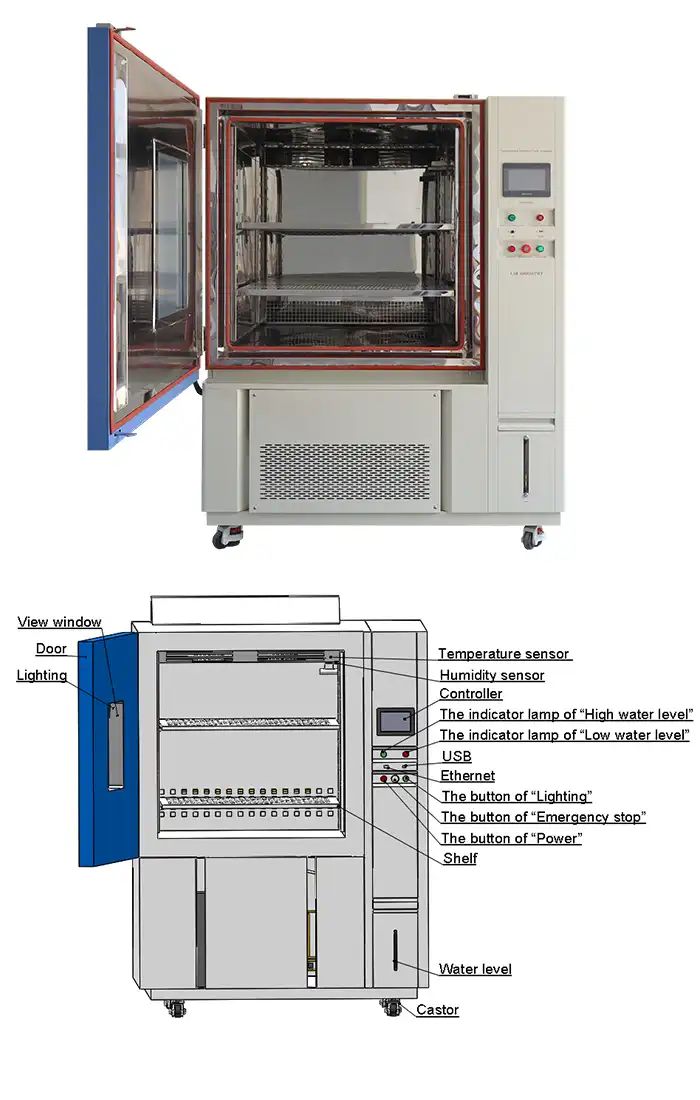
Shelf Life Test Chamber for Food Packaging Stability Testing
Ensuring food packaging performs reliably throughout its intended shelf life is critical to product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance. A shelf life test chamber enables manufacturers to evaluate packaging stability under precisely controlled temperature and humidity conditions that simulate real storage, transportation, and retail environments. By identifying material degradation, seal failures, and barrier performance changes early in development, companies can validate packaging designs with confidence before products reach the market.
A shelf life test chamber serves as an essential instrument for evaluating how food packaging performs under controlled environmental conditions over extended periods. These specialized chambers simulate various temperature and humidity scenarios that products might encounter during storage, transportation, and retail display. By accelerating aging processes through precise climate control, manufacturers can predict packaging degradation, identify potential failure points, and validate barrier properties before products reach consumers. This testing approach helps ensure that food packaging maintains its protective qualities throughout the intended shelf life, safeguarding product quality, consumer safety, and brand reputation.
What Factors Affect Food Packaging Stability?
Environmental Stress Variables
Food packaging faces multiple environmental challenges that impact its protective capabilities. Temperature extremes can cause materials to expand, contract, or degrade at varying rates. Polymers may become brittle in cold conditions while adhesives might soften under heat. Humidity levels directly influence moisture barrier performance, affecting seal integrity and material dimensional stability.
expand, contract, or degrade at varying rates. Polymers may become brittle in cold conditions while adhesives might soften under heat. Humidity levels directly influence moisture barrier performance, affecting seal integrity and material dimensional stability.
Chemical Interactions and Migration
Packaging materials can undergo chemical changes when exposed to certain food components or atmospheric gases. Oxygen permeation rates affect oxidative rancidity in fats and oils. Volatile organic compounds from packaging may migrate into food products, potentially altering taste profiles or raising safety concerns about compliance with regulatory standards.
Mechanical Degradation Pathways
Physical stresses accumulate during handling, stacking, and transportation. Flexural fatigue weakens seal areas while compression forces test structural integrity. Repeated thermal cycling creates stress points where cracks may initiate. Understanding these mechanical degradation patterns helps designers create more resilient packaging solutions.
Role of Temperature and Humidity in Shelf Life TestingPrecise Climate Control Requirements
Accurate environmental simulation demands tight control over temperature fluctuation and humidity distribution. Advanced shelf life test chambers maintain stability within ±0.5°C and carefully regulate moisture levels from 20% to 98% RH. This precision ensures reproducible results that accurately reflect real-world storage conditions rather than introducing variability from equipment limitations.
Thermal Cycling Protocols
Repeated temperature transitions reveal weaknesses that steady-state conditions might miss. Cycling between extreme temperatures stresses seal interfaces, tests adhesive bonds, and exposes material incompatibilities. Heating rates of 3°C/min and controlled cooling enable realistic simulation of daily temperature variations or seasonal changes.
Humidity Impact Assessment
Moisture significantly affects packaging performance across multiple dimensions. High humidity challenges barrier films, tests seal integrity against water vapor transmission, and accelerates corrosion of metal components. Low humidity conditions assess brittleness and static electricity generation in protective films.
Parameter | TH-225 Model | TH-500 Model |
Internal Dimensions | 500×600×750 mm | 700×800×900 mm |
Temperature Range | -86°C to +150°C | -86°C to +150°C |
Humidity Range | 20%-98% RH | 20%-98% RH |
Temperature Deviation | ±2.0°C | ±2.0°C |
Accelerated Aging for Food ProductsTime Compression Methodology
Accelerated aging applies elevated stress levels to compress months or years of natural aging into weeks of testing. The Arrhenius equation provides mathematical relationships between temperature elevation and reaction rate acceleration. This scientific approach enables rapid validation of packaging performance predictions without waiting for real-time aging completion.
Q10 Factor Applications
The Q10 relationship describes how reaction rates typically double with every 10°C temperature increase. Packaging engineers use this principle to calculate equivalent aging periods at elevated temperatures. Testing at 40°C for one month might simulate six months at ambient conditions, depending on specific material characteristics.
Validation Against Real-Time Data
Accelerated testing requires correlation with actual shelf life observations to ensure accuracy. Manufacturers typically run parallel studies comparing accelerated results with real-time aging samples. This validation confirms that elevated stress conditions produce degradation mechanisms similar to natural aging rather than introducing artificial failure modes.
Monitoring Packaging Integrity over Time
| Name | shelf life test chamber | |||||
Model | TH-100 | |||||
Internal dimension (mm) | 400*500*500 | |||||
Overall dimension (mm) | 860*1050*1620 | |||||
Capacity | 100L | |||||
Temperature range | -20℃ ~+150 ℃ | |||||
Low type | A: -40℃ B:-70℃ C -86℃ | |||||
Humidity Range | 20%-98%RH | |||||
Temperature deviation | ± 2.0 ℃ | |||||
Heating rate | 3 ℃ / min | |||||
Cooling rate | 1 ℃ / min | |||||
Controller | Programmable color LCD touch screen controller, Multi-language interface, Ethernet , USB | |||||
Exterior material | Steel Plate with protective coating | |||||
Interior material | SUS304 stainless steel | |||||
Standard configuration | 1 Cable hole (Φ 50) with plug; 2 shelves | |||||
Timing Function | 0.1~999.9 (S,M,H) settable | |||||
Visual Inspection Protocols
Regular examination reveals surface changes, discoloration, delamination, or physical deformation. Trained observers document seal appearance, material transparency, and any visible defects. Photographic documentation creates objective records for comparison across testing intervals and between different packaging configurations.
Instrumental Measurement Techniques
Quantitative assessments provide objective data about packaging performance changes when samples are evaluated in a shelf life test chamber. Tensile testing measures mechanical strength degradation while gas chromatography detects permeability increases. Seal strength analyzers evaluate bond integrity at multiple time points throughout accelerated aging cycles.
Barrier Property Evaluation
Oxygen transmission rates, water vapor permeability, and aromatic compound retention define packaging protective capabilities. Specialized instruments measure these parameters before and after environmental exposure. Degradation patterns help predict when barrier properties might fall below acceptable thresholds during actual distribution.
Test Parameter | Measurement Method | Acceptance Criteria |
Seal Strength | Tensile Testing | >15 N/15mm width |
Oxygen Transmission | Gas Chromatography | <50 cc/m²/day |
Water Vapor Permeability | Gravimetric Method | <5 g/m²/day |
Impact of Material Selection on Product Shelf LifePolymer Compatibility Considerations
Different plastic resins exhibit unique responses to environmental stresses. Polyethylene maintains flexibility across wide temperature ranges while polypropylene offers superior moisture barriers. Polyester provides excellent oxygen resistance but may become brittle under UV exposure. Matching material properties to product requirements optimizes protective performance.
Multi-Layer Structure Advantages
Combining materials with complementary properties creates superior barriers. Aluminum foil layers block light and provide exceptional oxygen barriers. Ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymers enhance gas resistance while polyethylene layers ensure heat sealability. Adhesive layers must maintain cohesion throughout temperature and humidity cycling.

Sustainable Material Challenges
Bio-based and compostable packaging materials present unique testing challenges. These materials may degrade intentionally under certain conditions while maintaining protection during intended shelf life. Chamber testing validates that degradation occurs only under appropriate composting conditions rather than during normal storage.
Predictive Analysis for Food Product QualityStatistical Modeling Approaches
Regression analysis correlates environmental exposure with packaging performance metrics. Weibull distributions predict failure probabilities across product populations. These statistical tools transform shelf life test chamber test data into actionable shelf life predictions with defined confidence intervals.
across product populations. These statistical tools transform shelf life test chamber test data into actionable shelf life predictions with defined confidence intervals.
Arrhenius Kinetics Application
Temperature-dependent degradation rates follow predictable mathematical relationships. Plotting degradation data against inverse absolute temperature yields activation energies for specific failure mechanisms. These calculations enable extrapolation from accelerated conditions to estimate performance at lower storage temperatures.
Risk Assessment Integration
Combining packaging degradation data with microbiological growth models provides comprehensive safety predictions. Understanding how barrier failure correlates with pathogen growth or toxin formation helps establish conservative shelf life limits. This integrated approach balances quality maintenance with consumer safety priorities.
Storage Condition | Predicted Shelf Life | Confidence Level |
-18°C (Frozen) | 24 months | 95% |
4°C (Refrigerated) | 90 days | 95% |
25°C (Ambient) | 12 months | 90% |
Ensure Food Safety & Quality with LIB Industry's Precise Shelf Life Test ChamberAdvanced Climate Control Technology
LIB chambers incorporate R404A and R23 refrigerants for ultra-low temperature capabilities reaching -86°C. Programmable touchscreen controllers with multi-language interfaces simplify complex testing protocols. Forced air convection systems distribute temperature uniformly throughout the testing space, eliminating hot spots that could compromise data integrity.
throughout the testing space, eliminating hot spots that could compromise data integrity.
Customizable Testing Solutions
Beyond standard configurations, LIB offers specialized modifications including explosion-proof designs for volatile product testing, low-pressure simulation for high-altitude distribution scenarios, and integrated vibration platforms for transportation simulation. PT100Ω temperature sensors and precision humidity probes ensure measurement accuracy throughout extended testing campaigns.
Remote Monitoring Capabilities
Network connectivity enables real-time data access via Ethernet or laboratory Wi-Fi systems. Researchers can monitor ongoing tests, receive alerts about parameter deviations, and download results through USB interfaces. This connectivity supports multi-site collaboration and enables continuous oversight without constant physical presence.
Maintenance and Cleaning Efficiency
Mirror-finish stainless steel interiors resist corrosion while simplifying sanitation after tests involving food spoilage. Perforated shelving allows drainage and air circulation while supporting diverse sample configurations. Separate water and electrical systems enhance operational safety during cleaning procedures and routine maintenance activities.
Conclusion
Shelf life test chambers provide critical validation tools for ensuring food packaging maintains protective qualities throughout distribution cycles. Through precise environmental control, accelerated aging protocols, and comprehensive monitoring approaches, manufacturers gain confidence that their packaging solutions will perform reliably. Advanced chamber technology from specialized manufacturers enables thorough evaluation of material performance, seal integrity, and barrier properties under conditions that accurately simulate real-world challenges.
FAQsHow long does accelerated shelf life testing typically take?
Accelerated testing duration depends on target shelf life and acceleration factors applied. Most food packaging studies require 3-12 weeks of chamber testing to simulate 6-24 months of real-time aging, with validation studies running parallel real-time controls.
Can shelf life chambers test multiple packaging formats simultaneously?
Modern chambers accommodate diverse sample configurations on adjustable shelving systems. Researchers can test pouches, bottles, trays, and cartons within the same run, provided all samples require identical environmental conditions and testing protocols throughout the study period.
What maintenance requirements do shelf life test chambers have?
Regular maintenance includes refrigerant level verification, sensor calibration verification, cleaning of condensate drains, and inspection of door seals. Most manufacturers recommend professional calibration annually, with routine cleaning after each test cycle involving potentially contaminating samples.
Partner with LIB Industry for Your Testing Needs
As a leading shelf life test chamber manufacturer and supplier, LIB Environmental Simulation Industry delivers precision equipment backed by comprehensive technical support. Our factory produces CE-approved chambers designed for demanding food packaging applications. Contact our team at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss your specific testing requirements and receive detailed quotations for standard or custom configurations.