Shelf Life Test Chamber for Temperature and Humidity Cosmetic Testing
Imagine your cosmetic or food product quietly aging on a store shelf—enduring summer heat, winter cold, and fluctuating humidity long before it ever reaches the consumer. A shelf life test chamber makes this invisible journey visible, simulating real-world storage conditions to uncover formulation weaknesses, packaging risks, and long-term stability challenges before market launch.
This performance is already being validated in real laboratories. A Canadian lab using the TH-1000C shelf life test chamber shared early feedback: “Hi Karen, we have been using the chamber since last week. It is overall good so far. I will keep you updated.” Such real-world confidence highlights the reliability and consistency required for cosmetic stability testing. Let’s explore how shelf life test chambers safeguard product quality, safety, and brand trust.
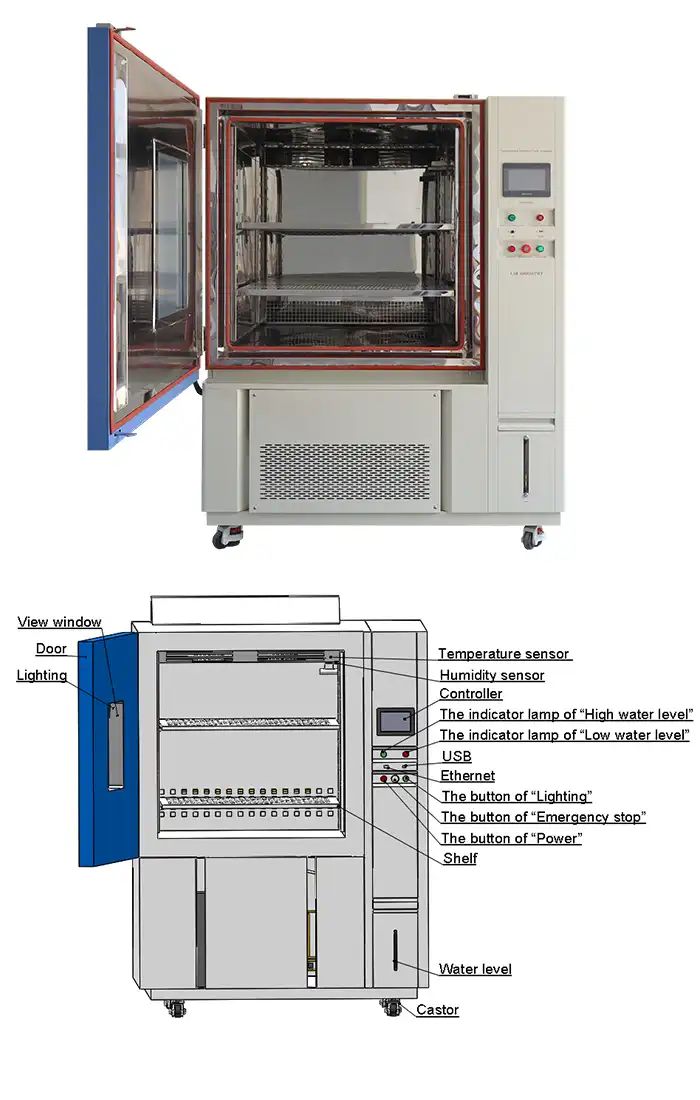
A shelf life test chamber designed for cosmetic testing simulates real-world storage conditions to evaluate product stability over time. These specialized environmental chambers control temperature (-40°C to +150°C) and humidity (20%-98% RH) to replicate months or years of aging within weeks. By exposing cosmetics to accelerated conditions, manufacturers can predict shelf life, identify formulation weaknesses, verify packaging integrity, and ensure regulatory compliance before market launch. This testing validates that products maintain their safety, efficacy, and aesthetic qualities throughout their intended lifespan, protecting both brand reputation and consumer trust.
Why Cosmetics Require Stability Testing?
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Cosmetic manufacturers worldwide face stringent regulatory frameworks that mandate stability testing before product distribution. The FDA's Cosmetic Voluntary Registrations Program and the EU's Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 require documented evidence of product safety and quality maintenance. A shelf life test chamber provides the controlled environment necessary to generate this compliance data, demonstrating that formulations remain within acceptable specifications throughout their declared period after opening (PAO). Testing protocols typically span 12-36 months under various stress conditions, with chambers providing reproducible results that satisfy regulatory auditors.
Registrations Program and the EU's Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 require documented evidence of product safety and quality maintenance. A shelf life test chamber provides the controlled environment necessary to generate this compliance data, demonstrating that formulations remain within acceptable specifications throughout their declared period after opening (PAO). Testing protocols typically span 12-36 months under various stress conditions, with chambers providing reproducible results that satisfy regulatory auditors.
Consumer Safety Considerations
Degraded cosmetics pose significant health risks ranging from skin irritation to microbial contamination. Temperature and humidity fluctuations accelerate chemical reactions that can transform safe ingredients into sensitizing compounds. Preservative systems may lose efficacy, allowing bacterial or fungal growth that threatens user safety. Environmental simulation chambers expose products to worst-case scenarios - tropical heat, freezing winters, humid coastal climates - revealing vulnerabilities before consumers encounter them. This proactive approach prevents recalls, liability claims, and reputational damage while safeguarding public health.
Market Competition and Brand Protection
Premium cosmetic brands differentiate themselves through guaranteed product performance across global markets. Stability testing validates claims about texture retention, fragrance longevity, and color consistency that justify higher price points. Chambers enable comparative testing against competitor formulations, identifying competitive advantages or necessary improvements. Documented stability data becomes a marketing asset, supporting claims of superior quality and providing technical ammunition for B2B negotiations with retailers demanding shelf life guarantees.
Effects of Heat and Moisture on Cosmetic ProductsChemical Degradation Pathways
Elevated temperatures accelerate oxidative reactions that destabilize active ingredients and cause color shifts. Retinol converts to inactive isomers, vitamin C degrades to dehydroascorbic acid, and essential oils lose volatile components. Humidity introduces water activity that hydrolyzes esters, disrupts emulsions, and enables Maillard browning reactions. A controlled shelf life test chamber replicates these conditions with precision, using PT100Ω temperature probes and humidity sensors to maintain exact parameters. The programmable touchscreen controller cycles between stress conditions, simulating diurnal temperature variations and seasonal humidity changes that reveal formulation resilience.
Physical Stability Changes
Heat reduces viscosity in creams and lotions, causing phase separation where oil and water components divorce. Cold temperatures induce crystallization in lipid-based products, creating grainy textures. Humidity affects powder compacts through moisture absorption, causing clumping or microbial growth. Environmental chambers equipped with forced air convection systems ensure uniform conditions throughout the testing space, eliminating hot spots that could produce misleading results. The mirror-finished stainless steel interiors reflect heat evenly while simplifying cleanup after inevitable product spillage.
Microbial Challenge Response
Temperature and humidity directly influence preservative efficacy and microbial survival rates. Chambers operating at 30°C/75% RH replicate tropical conditions where bacteria and fungi thrive, challenging antimicrobial systems to their limits. Conversely, freeze-thaw cycling tests packaging seal integrity and preservative distribution after temperature shock. Multi-cycle testing protocols in advanced chambers reveal whether preservative systems maintain minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) against common cosmetic contaminants like Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans throughout the product lifecycle.
| Name | shelf life test chamber | |||||
Model | TH-100 | |||||
Temperature range | -20℃ ~+150 ℃ | |||||
Low type | A: -40℃ B:-70℃ C -86℃ | |||||
Humidity Range | 20%-98%RH | |||||
Temperature deviation | ± 2.0 ℃ | |||||
Heating rate | 3 ℃ / min | |||||
Cooling rate | 1 ℃ / min | |||||
Controller | Programmable color LCD touch screen controller, Multi-language interface, Ethernet , USB | |||||
Exterior material | Steel Plate with protective coating | |||||
Interior material | SUS304 stainless steel | |||||
Standard configuration | 1 Cable hole (Φ 50) with plug; 2 shelves | |||||
Timing Function | 0.1~999.9 (S,M,H) settable | |||||
Packaging Evaluation for Cosmetic Shelf LifeContainer Material Compatibility
Packaging materials respond dynamically to environmental stresses, potentially contaminating products or failing structurally. Plastic containers may leach plasticizers at elevated temperatures, while metals can corrode under humid conditions. Glass shows minimal reactivity but risks thermal shock cracking. Shelf life chambers with temperature ranges from -86°C to +150°C test packaging across extreme conditions, revealing material limitations before mass production commitments. Sample shelves constructed from perforated #304 stainless steel accommodate various container sizes while ensuring air circulation around each test specimen.
Seal Integrity and Barrier Properties
Moisture vapor transmission rates (MVTR) and oxygen permeability determine how quickly external conditions affect product quality. Chamber testing quantifies these barrier properties under stress, measuring weight changes that indicate moisture ingress or volatile loss. Airless pumps, droppers, and spray mechanisms undergo functional testing after temperature cycling to ensure dispensing accuracy. The TH-225 and TH-500 models offer sufficient internal dimensions (500×600×750mm and 700×800×900mm respectively) to accommodate full product packaging rather than just formulation samples.
Parameter | TH-225 Model | TH-500 Model |
Internal Dimensions | 500×600×750 mm | 700×800×900 mm |
Temperature Range | -86°C to +150°C | -86°C to +150°C |
Humidity Range | 20%-98% RH | 20%-98% RH |
Temperature Deviation | ±2.0°C | ±2.0°C |
Label and Print Durability
Product labeling conveys critical safety information that must remain legible throughout shelf life. Humidity causes adhesive failure, ink bleeding, and paper delamination. UV exposure fades colors while heat accelerates adhesive degradation. Shelf life test chambers simulate these combined stresses, revealing whether regulatory warnings, ingredient lists, and brand graphics survive realistic storage and distribution scenarios. Testing prevents marketplace failures where illegible labels trigger regulatory violations or consumer confusion.
Accelerated Aging Methods in CosmeticsQ10 Temperature Coefficient Calculations
The Arrhenius equation provides the mathematical foundation for accelerated aging, where each 10°C temperature increase approximately doubles reaction rates (Q10 ≈ 2). Chambers operating at 40°C simulate roughly 6-12 months of room temperature aging per month of testing, depending on specific reaction kinetics. Precise temperature control within ±0.5°C fluctuation ensures reliable extrapolation from accelerated to real-time conditions. Programmable controllers execute complex temperature profiles that alternate stress periods with recovery intervals, mimicking seasonal variations more accurately than constant-temperature protocols.
ICH Stability Testing Guidelines
The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) establishes globally recognized testing conditions including 25°C/60% RH (Zone II, temperate climates) and 30°C/65% RH (Zone IVa, hot/humid climates). Advanced shelf life chambers store multiple ICH protocols simultaneously, with independent compartments maintaining different conditions. The environmentally friendly R404A and R23 refrigerants provide efficient cooling across the -86°C to +150°C operational range while complying with environmental regulations. Ethernet connectivity allows remote monitoring of multiple ongoing studies, with automatic alerts when parameters drift beyond specifications.
Photostability Testing Integration
While traditional chambers focus on temperature and humidity, comprehensive stability programs include light exposure simulating retail display conditions. Some customized units integrate UV/visible light sources alongside climate control, enabling simultaneous photo-degradation and thermal stress testing. The USB data logging capability captures minute-by-minute conditions, providing the documentation trail regulators demand. Multi-language touchscreen interfaces accommodate international research teams collaborating on global product launches.
Testing Condition | Climate Zone | Typical Duration | Purpose |
25°C / 60% RH | Zone II (Temperate) | 12-36 months | Standard shelf life validation |
30°C / 65% RH | Zone IVa (Hot/Humid) | 6-12 months | Tropical market qualification |
40°C / 75% RH | Accelerated | 3-6 months | Challenge testing |
Ensuring Product Safety and PerformanceActive Ingredient Potency Maintenance
Cosmeceutical products containing pharmaceutical-grade actives require validated stability proving therapeutic concentrations persist until expiration. Peptides undergo hydrolysis, antioxidants sacrifice themselves neutralizing free radicals, and enzymes denature under stress. Shelf life test chamber testing with regular sampling intervals (0, 1, 3, 6, 12 months) generates degradation curves showing potency over time. Analytical methods like HPLC quantify remaining active concentrations, determining whether products maintain minimum effective doses throughout their claimed shelf life. This data supports labeling accuracy and therapeutic claims.
undergo hydrolysis, antioxidants sacrifice themselves neutralizing free radicals, and enzymes denature under stress. Shelf life test chamber testing with regular sampling intervals (0, 1, 3, 6, 12 months) generates degradation curves showing potency over time. Analytical methods like HPLC quantify remaining active concentrations, determining whether products maintain minimum effective doses throughout their claimed shelf life. This data supports labeling accuracy and therapeutic claims.
Sensory Attribute Preservation
Consumer acceptance depends heavily on sensory experiences - fragrance, color, texture, and application feel. Heat accelerates fragrance note development and evaporation, shifting top notes to base notes prematurely. Emulsion breakdown produces separated layers or grainy textures. Color changes from oxidation signal quality degradation even when products remain safe. Trained sensory panels evaluate chamber-aged samples against fresh controls, quantifying perceptible differences using standardized scoring systems. Products failing sensory benchmarks before expiration dates require reformulation regardless of safety test passage.
Consistency Across Production Batches
Stability testing isn't merely a development activity - ongoing quality assurance programs test representative samples from each production batch. Chamber archives retain reserve samples from every batch, enabling retrospective investigation when customer complaints arise. The independent water and electrical systems in LIB chambers ensure continuous operation even during maintenance, preventing testing interruptions that could delay product releases. Remote control capabilities via laboratory networks allow quality managers to monitor multiple chambers across different facilities simultaneously.
Quality Control Metrics for Cosmetic StabilityPhysical Property Measurements
Objective testing protocols measure viscosity changes, pH drift, specific gravity variations, and particle size distributions. Rheological testing reveals how creams and lotions flow and spread, critical parameters affecting consumer perception and application effectiveness. pH monitoring detects formulation instability or preservative breakdown, with acceptable ranges typically within ±0.5 pH units of initial values. Color spectrophotometers quantify Lab values, detecting subtle shifts invisible to untrained observers. Chambers provide the stable baseline conditions necessary for reproducible measurements across testing timepoints.
Microbiological Stability Indicators
Preservative challenge testing exposes aged samples to standardized microbial inocula (bacteria, yeast, mold) to verify antimicrobial system functionality. Pass criteria require specific log reductions within defined timeframes - typically 2-log reduction within 14 days for bacteria, 1-log for fungi. Total viable count (TVC) testing throughout stability studies detects contamination from inadequate preservation or packaging failures. The easy-to-clean mirror stainless steel interiors with punch-hole drainage design prevent microbial reservoirs within chambers that could cross-contaminate test samples.
Analytical Chemistry Validation
Gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and spectroscopic methods identify degradation products, preservative concentrations, and fragrance component levels. Stability-indicating assays distinguish active ingredients from degradation products, quantifying both desired compounds and potentially harmful breakdown products. Acceptance criteria established during development define acceptable ranges for each measured parameter. Chamber-generated samples feed systematic analytical programs producing the documentation chains regulatory agencies scrutinize during pre-market reviews and post-market surveillance.
Quality Metric | Testing Method | Acceptance Criteria | Frequency |
Viscosity | Brookfield Rheometer | ±20% of initial value | 0, 3, 6, 12 months |
pH Level | Electrode Measurement | ±0.5 pH units | 0, 3, 6, 12 months |
Color Stability | Spectrophotometry | ΔE < 2.0 | 0, 3, 6, 12 months |
Preservative Content | HPLC Analysis | >80% of label claim | 0, 6, 12 months |
Preserve Cosmetic Integrity with LIB Industry's Controlled Shelf Life Test ChamberAdvanced Technical Specifications
LIB Environmental Simulation Industry delivers shelf life test chambers combining precision control with operational reliability. The forced air convection system produces uniform temperature distribution eliminating dead zones that compromise test validity. High-precision PT100Ω sensors monitor conditions with minimal drift, maintaining ±2.0°C temperature deviation across the entire workspace. Heating rates of 3°C/min and cooling rates of 1°C/min enable efficient protocol cycling without thermal overshoot. The programmable color LCD touchscreen controller accommodates complex multi-stage protocols with intuitive menu navigation, reducing operator training requirements.
Customization and Integration Capabilities
LIB's engineering team configures chambers matching specific testing requirements through extensive customization options. Explosion-proof modifications accommodate volatile formulations, low-pressure simulation replicates high-altitude distribution environments, and integrated vibration systems combine transport stress with climate exposure. The standard network ports enable seamless integration into laboratory information management systems (LIMS), automatically logging data and triggering alerts when parameters deviate. Water level observation windows and independent water/electrical system architecture enhance safety while simplifying maintenance. Multiple refrigerant options (-40°C, -70°C, -86°C low-temperature configurations) serve diverse testing needs from standard cosmetics to specialty products requiring extreme cold exposure.
Comprehensive Support and Validation
Beyond equipment manufacturing, LIB provides turnkey solutions encompassing installation, commissioning, operator training, and ongoing technical support. CE certification demonstrates compliance with European safety standards, while factory acceptance testing (FAT) and site acceptance testing (SAT) validate performance before customer acceptance. Calibration certificates traceable to national standards accompany each chamber, establishing measurement confidence for regulatory submissions. Extended service contracts include preventive maintenance, calibration verification, and emergency response, ensuring continuous operation supporting critical stability programs. The global support network delivers responsive technical assistance regardless of installation location, protecting research investments and project timelines.
Conclusion
Shelf life test chambers represent indispensable infrastructure for cosmetic manufacturers committed to quality, safety, and regulatory compliance. By simulating diverse environmental conditions with precision control, these systems predict product performance across global markets and storage scenarios. The investment in validated stability testing prevents costly recalls, protects brand reputation, and demonstrates commitment to consumer safety. LIB Industry's comprehensive chamber solutions deliver the technical capabilities, customization flexibility, and ongoing support necessary for rigorous cosmetic stability programs meeting international standards.
FAQsHow long does cosmetic stability testing typically require in a shelf life test chamber?
Standard testing protocols run 12-36 months for real-time studies, while accelerated testing at elevated temperatures compresses this timeline to 3-6 months. The specific duration depends on intended shelf life claims, regulatory requirements, and product complexity. Multiple timepoint sampling throughout testing generates comprehensive degradation profiles.
What temperature and humidity conditions should cosmetics be tested under?
ICH guidelines recommend 25°C/60% RH for temperate climates and 30°C/65% RH for hot/humid regions as primary conditions. Accelerated testing typically employs 40°C/75% RH, while stress testing may include freeze-thaw cycling and extreme temperatures up to 50°C. Testing should reflect the harshest conditions expected during distribution and storage.
Can one chamber test multiple product formulations simultaneously?
Yes, shelf life chambers accommodate numerous samples simultaneously through adjustable shelving systems. However, all samples within a chamber experience identical conditions. Testing products requiring different climate protocols necessitates multiple chambers or sequential testing programs. Sample placement should ensure adequate air circulation and avoid cross-contamination between formulations.
Partner with LIB Industry, a leading shelf life test chamber manufacturer and supplier, to ensure your cosmetic products maintain integrity throughout their lifecycle. Contact our technical team at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss customized testing solutions for your specific formulation and packaging requirements.