Temperature Performance Testing of Equipment in Hot and Cold Chambers
Temperature performance testing in hot and cold chambers is a fundamental validation step for instruments and equipment required to operate reliably across extreme climatic conditions. By exposing products to controlled high- and low-temperature environments, manufacturers can verify functional stability, detect thermal vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with international standards. Such testing is especially critical for precision instruments, where temperature-induced drift or material stress can directly affect measurement accuracy and long-term reliability.
Proven performance in real customer applications further reinforces the value of this testing approach. A Russian customer specializing in instrument testing recently confirmed that after installation, the temperature-humidity chamber has been operating smoothly, noting that the chamber is currently in use and all functions are working well. This positive feedback highlights how a stable and reliable hot and cold chamber becomes an essential tool from day one—supporting routine temperature performance testing while providing confidence in data accuracy and operational continuity.
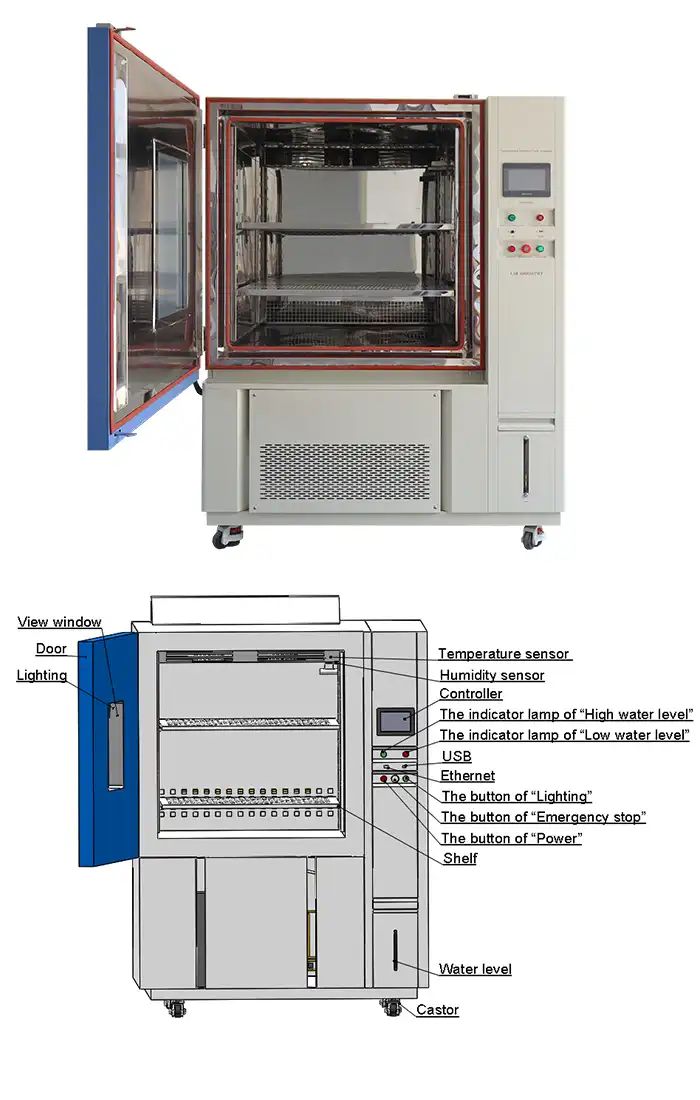
Temperature performance testing in hot and cold chambers represents a critical validation process where equipment undergoes controlled thermal exposure to verify functionality across designated operating ranges. These specialized environmental chambers simulate extreme temperature fluctuations, enabling manufacturers to assess product durability, identify potential failure modes, and ensure compliance with international standards. Through systematic testing protocols, engineers can replicate years of thermal stress within compressed timeframes, delivering comprehensive performance data that guides design improvements and quality assurance decisions.
Why Equipment Needs Temperature Performance Testing?
Protecting Product Integrity Across Climates
Modern equipment must function reliably whether deployed in Arctic research stations or desert manufacturing facilities. Temperature variations directly impact material properties, component tolerances, and electronic performance characteristics. Without rigorous validation, products risk catastrophic failures when exposed to environmental conditions beyond their tested capabilities.
Temperature variations directly impact material properties, component tolerances, and electronic performance characteristics. Without rigorous validation, products risk catastrophic failures when exposed to environmental conditions beyond their tested capabilities.
Reducing Warranty Claims and Field Failures
Undiscovered thermal weaknesses translate directly into customer dissatisfaction and financial losses. Testing identifies vulnerabilities before mass production, allowing engineering teams to implement corrective measures. This proactive approach minimizes costly recalls and protects brand reputation within competitive markets.
Meeting Customer Expectations for Reliability
End users increasingly demand equipment that performs consistently regardless of installation location. Temperature testing provides tangible evidence of reliability, supporting marketing claims with verified data. Organizations that demonstrate thorough environmental validation gain competitive advantages when pursuing contracts requiring proven performance credentials.
Evaluating Operational Limits under Extreme Conditions
Establishing Minimum and Maximum Temperature Thresholds
Engineers systematically expose equipment to progressively severe temperatures, documenting the precise points where performance degradation begins. This data establishes operational boundaries that inform specification sheets and user documentation. Understanding these limits prevents equipment deployment in unsuitable environments.
performance degradation begins. This data establishes operational boundaries that inform specification sheets and user documentation. Understanding these limits prevents equipment deployment in unsuitable environments.
Assessing Recovery Capabilities After Thermal Exposure
Beyond identifying failure points, testing reveals how quickly equipment returns to normal operation following extreme temperature events. Recovery speed indicates thermal resilience and helps predict performance in environments with rapid temperature swings, such as industrial facilities with intermittent heating systems.
Characterizing Performance Degradation Patterns
Detailed monitoring during testing in a hot and cold chamber reveals whether equipment fails suddenly or experiences gradual performance decline. This characterization enables predictive maintenance strategies and helps manufacturers determine appropriate derating factors for operation near temperature limits.
Thermal Cycling Tests for Reliability Assessment
Simulating Real-World Temperature Fluctuations
Thermal cycling replicates the expansion and contraction stresses equipment experiences during actual service. These repeated transitions reveal solder joint fatigue, seal degradation, and interface failures that might not appear during static temperature exposure. Cycling tests accelerate aging processes, compressing months of field operation into weeks.
Identifying Material Compatibility Issues
Different materials expand at varying rates when heated, creating mechanical stress at component interfaces. Cycling tests expose mismatches in thermal expansion coefficients that cause delamination, cracking, or connection failures. Early identification allows material substitutions or design modifications before production commitments.
Validating Assembly Process Robustness
Manufacturing variations affect how products withstand thermal stress. Testing production samples rather than prototypes validates that assembly processes consistently produce thermally resilient units. This verification ensures quality control measures effectively maintain temperature performance standards across manufacturing runs.
Monitoring Performance Metrics under Heat and Cold Stress
Tracking Electrical Parameter Variations
Electronic components exhibit temperature-dependent characteristics affecting circuit performance. Voltage outputs drift, resistance values change, and semiconductor properties vary with temperature. Continuous monitoring during chamber testing quantifies these variations, enabling compensation circuit design and tolerance specification.
| Name | hot and cold chambers | |||||
Model | TH-100 | |||||
Temperature range | -20℃ ~+150 ℃ | |||||
Low type | A: -40℃ B:-70℃ C -86℃ | |||||
Humidity Range | 20%-98%RH | |||||
Temperature deviation | ± 2.0 ℃ | |||||
Heating rate | 3 ℃ / min | |||||
Cooling rate | 1 ℃ / min | |||||
Controller | Programmable color LCD touch screen controller, Multi-language interface, Ethernet , USB | |||||
Exterior material | Steel Plate with protective coating | |||||
Interior material | SUS304 stainless steel | |||||
Standard configuration | 1 Cable hole (Φ 50) with plug; 2 shelves | |||||
Timing Function | 0.1~999.9 (S,M,H) settable | |||||

Measuring Mechanical Dimension Changes
Thermal expansion causes dimensional variations that impact precision equipment, optical systems, and mechanical assemblies. High-precision measurement during temperature excursions in a hot and cold chamber documents expansion coefficients and helps establish acceptable operating tolerances for applications requiring dimensional stability.
Recording Response Time and Functionality
Equipment responsiveness often varies with temperature as lubricants thicken, materials stiffen, or electronic speeds change. Testing documents how temperature affects startup times, processing speeds, and mechanical actuation rates. This data informs user expectations and helps define performance specifications.
Performance Metric | Cold Stress Impact | Heat Stress Impact |
Electrical Resistance | Decreased values | Increased values |
Mechanical Viscosity | Increased friction | Reduced lubricant effectiveness |
Battery Capacity | Significant reduction | Moderate reduction |
Sensor Accuracy | Baseline shifts | Increased noise levels |
Predicting Equipment Failures and Maintenance Needs
Accelerated Life Testing Through Temperature Stress
Elevated temperatures accelerate chemical reactions and mechanical wear processes, enabling lifetime predictions based on relatively short test durations. The Arrhenius equation relates temperature to reaction rates, providing mathematical frameworks for extrapolating test results to field conditions and estimating service life.
Identifying Weak Components Requiring Redesign
Testing reveals which subsystems fail first under thermal stress, directing engineering attention toward vulnerable areas. Component-level failure analysis determines root causes, whether material selection, manufacturing defects, or design inadequacies. This focused approach optimizes development resources.
Developing Condition-Based Maintenance Schedules
Understanding how temperature exposure affects equipment health enables maintenance planning based on actual operating conditions rather than arbitrary time intervals. Equipment experiencing severe thermal cycles requires more frequent inspection than units operating within narrow temperature ranges, improving maintenance efficiency.
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards
Meeting International Testing Protocols
Organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and Military Standards (MIL-STD) specify temperature testing requirements for various product categories. Compliance demonstrates adherence to recognized engineering practices and facilitates market access in regulated industries. Chambers must meet calibration standards to produce legally defensible test results.
Achieving Regulatory Certifications
Medical devices, aerospace components, and automotive systems require temperature qualification as part of regulatory approval processes. Testing documentation provides evidence supporting certification applications, demonstrating that products meet safety and performance requirements across their rated temperature ranges.
Supporting Quality Management Systems
ISO 9001 and similar quality frameworks require validation of product performance claims. Temperature testing generates objective evidence that products meet specifications, supporting audit requirements and demonstrating continuous improvement commitment. Documented testing procedures ensure repeatability and traceability.
Industry Standard | Temperature Range | Typical Test Duration |
IEC 60068-2-1 (Cold) | -40°C to -70°C | 16-96 hours |
IEC 60068-2-2 (Heat) | +85°C to +150°C | 16-96 hours |
MIL-STD-810H | -60°C to +125°C | Mission-dependent |
Validate Equipment Under Extreme Conditions with LIB Industry's Hot and Cold Chamber
Advanced Temperature Control Technology
LIB Industry's hot and cold chambers utilize French TECUMSEH compressors and precision programmable controllers delivering temperature stability within ±0.5°C. This accuracy ensures test conditions remain consistent throughout extended trials, producing reliable data. Multiple temperature range options from -20°C to -70°C minimum temperatures accommodate diverse testing requirements.
Comprehensive Testing Capabilities
Beyond basic temperature control, LIB chambers integrate humidity management (20-98% RH), enabling combined environmental stress testing. The modular design supports vibration, altitude, and pressure testing integration, creating comprehensive validation environments. Stainless steel construction resists corrosion while maintaining cleanliness standards required for pharmaceutical and food industry applications.
Complete Solution and Support Services
LIB Industry provides turnkey solutions encompassing design consultation, installation, operator training, and three-year warranties. Automatic water supply systems and programmable touch screen controllers reduce operator workload while Ethernet connectivity enables remote monitoring. Custom chamber configurations address unique testing requirements that standard models cannot accommodate.
Chamber Model | Internal Volume | Temperature Range | Application Focus |
TH-100 | 100L | -40°C to +150°C | Component testing |
TH-500 | 500L | -70°C to +150°C | Product assemblies |
TH-1000 | 1000L | -40°C to +150°C | Large equipment |
Conclusion
Temperature performance testing in hot and cold chambers provides essential validation data that protects product quality, ensures regulatory compliance, and builds customer confidence. Systematic evaluation of operational limits, thermal cycling resilience, and performance metrics under extreme conditions enables manufacturers to deliver reliable equipment suited to global deployment. Investment in comprehensive temperature testing reduces field failures, optimizes maintenance strategies, and demonstrates engineering excellence through objective performance verification.
FAQs
What temperature range should I specify for testing my equipment?
Select ranges matching your product's intended operating environment plus safety margins. Consider extreme conditions possible in deployment locations, typically adding 10-20°C beyond expected environmental limits for adequate validation coverage.
How long does typical temperature performance testing require?
Testing duration depends on product complexity and standards requirements. Basic qualification may require 48-96 hours, while accelerated life testing or regulatory compliance can extend to several weeks with multiple thermal cycles and extended exposure periods.
Can temperature chambers test multiple units simultaneously?
Chamber capacity determines simultaneous testing quantity. Ensure adequate spacing between units for proper air circulation and avoid thermal shadowing. Larger chambers like the TH-1000 accommodate multiple samples while maintaining uniform temperature distribution throughout the testing volume.
Secure Reliable Performance Data with Expert Testing Solutions
Partner with LIB Industry, your trusted hot and cold chamber manufacturer and supplier, to validate equipment performance under demanding thermal conditions. Contact our technical team at ellen@lib-industry.com for customized testing solutions.