Using Calibration Environmental Chambers in Electronics Testing
Using Calibration Environmental Chambers in Electronics Testing
Modern electronics face challenging operational environments, from scorching desert heat to frigid Arctic conditions. A calibration environmental chamber serves as the cornerstone for validating electronic reliability by recreating precise temperature and humidity scenarios. These sophisticated testing systems enable manufacturers to identify potential failures before products reach consumers, ensuring devices perform consistently across their intended operational spectrum. By subjecting electronics to controlled climatic stress, engineers gather critical performance data that drives design improvements and validates compliance with international quality benchmarks.

Importance of Temperature and Humidity Testing for Electronics
Understanding Thermal Stress on Electronic Components
Electronic components exhibit significant sensitivity to temperature variations. Semiconductors, capacitors, and resistors experience altered electrical characteristics when exposed to thermal extremes, potentially causing performance degradation or catastrophic failure. Thermal expansion and contraction cycles create mechanical stress on solder joints, circuit board traces, and component leads, leading to intermittent connections or complete circuit breaks.
Humidity's Impact on Device Longevity
Moisture penetration represents one of the most destructive forces affecting electronic assemblies. High humidity levels accelerate corrosion on metallic contacts, connectors, and circuit traces. Condensation can create conductive pathways between circuit elements, causing short circuits and leakage currents that compromise functionality. Hygroscopic materials within electronic packages absorb moisture, leading to dimensional changes and delamination.
Preventing Field Failures Through Accelerated Testing
Controlled environmental testing compresses months or years of operational exposure into concentrated test cycles. This accelerated aging process reveals latent defects and design weaknesses that might not surface during standard functional testing. Manufacturers significantly reduce warranty claims and field failures by identifying problematic components or assembly processes during development phases rather than after market release.
Common Electronic Components Tested in Chambers
Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits
Microprocessors, memory chips, and application-specific integrated circuits undergo rigorous environmental validation to ensure junction temperature limits remain within specification. Temperature cycling reveals packaging defects, wire bond integrity issues, and die attach problems. Humidity testing exposes hermetic seal failures and moisture sensitivity levels that determine proper handling and storage requirements.
Passive Components and Connectors
Capacitors demonstrate notable capacitance drift and equivalent series resistance changes across temperature ranges. Inductors and transformers experience core material property shifts affecting their electromagnetic behavior. Connectors undergo contact resistance testing under temperature and humidity stress to ensure reliable signal transmission and power delivery throughout the product lifecycle.
Printed Circuit Board Assemblies
Complete circuit board assemblies face comprehensive environmental screening to validate manufacturing quality. Thermal cycling stresses solder joints, revealing cold solder connections, insufficient fillet formation, or improper reflow profiles. Humidity exposure identifies inadequate conformal coating coverage, flux residue problems, and moisture-sensitive assembly processes that require correction.
Simulating Extreme Environmental Conditions for Devices
Replicating Real-World Operating Environments
Electronics destined for automotive applications must withstand engine compartment temperatures exceeding 125°C while maintaining functionality during winter cold starts at -40°C. Aerospace electronics face rapid altitude changes causing dramatic temperature swings. A calibration environmental chamber accurately reproduces these harsh conditions, enabling engineers to validate designs against actual deployment scenarios.
Creating Temperature and Humidity Profiles
Advanced calibration environmental chamber controllers execute complex test profiles combining temperature ramps, stabilization periods, and humidity variations. Typical automotive qualification profiles include multiple cycles between temperature extremes with controlled transition rates. Medical device testing often requires extended exposure at specific temperature and humidity combinations to validate sterilization resistance and storage stability.
Thermal Shock Testing Capabilities
Rapid temperature transitions identify components vulnerable to sudden environmental changes. Transfer time between hot and cold zones typically ranges from 10 to 30 seconds, creating severe thermal stress. This testing methodology effectively screens for packaging defects, material compatibility issues, and assembly process weaknesses that compromise product reliability.
Test Condition | Temperature Range | Typical Duration | Primary Purpose |
Operating Life Test | -40°C to +85°C | 1000-2000 hours | Long-term reliability validation |
Temperature Cycling | -55°C to +125°C | 500-1000 cycles | Solder joint and package integrity |
Humidity Bias Test | 85°C/85% RH | 1000 hours | Moisture resistance evaluation |
Reliability Testing Protocols for Electronic Products
Industry Standard Test Methods
International standards such as IEC 60068, MIL-STD-810, and JEDEC provide standardized test protocols ensuring consistent evaluation methodologies. These specifications define precise temperature profiles, humidity levels, test durations, and acceptance criteria. Compliance with recognized standards facilitates market acceptance and regulatory approval across global markets.
Highly Accelerated Life Testing (HALT)
HALT pushes devices beyond normal operational limits to quickly discover design margins and failure mechanisms. Progressive temperature steps combined with vibration stress identify the weakest elements within complex assemblies. This destructive testing approach provides valuable data for design optimization, enabling engineers to strengthen vulnerable areas before production qualification.
Environmental Stress Screening (ESS)
Production units undergo ESS protocols to precipitate latent manufacturing defects before customer shipment. Temperature cycling combined with functional testing during thermal dwells catches workmanship errors, marginal components, and assembly anomalies. Effective ESS significantly reduces early-life failures, improving customer satisfaction and reducing warranty expenses.
Qualification Testing Requirements
New product introductions require comprehensive qualification testing demonstrating design maturity and manufacturing capability. Sample sizes typically range from 30 to 100 units depending on statistical confidence requirements. Test sequences include temperature cycling, humidity exposure, thermal shock, and various operational stress combinations spanning several weeks or months.
Data Collection and Analysis in Electronics Testing
Automated Monitoring Systems
Modern calibration environmental chambers integrate with sophisticated data acquisition systems capturing temperature, humidity, electrical parameters, and functional test results. Real-time monitoring enables immediate detection of anomalies or failures during extended test sequences. Ethernet connectivity allows remote supervision and automatic alert notification when critical events occur.
Parameter Tracking and Trend Analysis
Continuous measurement of electrical characteristics throughout environmental exposure reveals gradual performance shifts indicating impending failures. Resistance measurements on connectors detect oxidation or contact degradation. Voltage reference drift in precision circuits identifies temperature coefficient problems. Leakage current monitoring exposes moisture-related insulation breakdown.
Failure Analysis Documentation
Comprehensive records of environmental conditions, electrical measurements, and failure observations support root cause investigations. Detailed documentation enables correlation between specific test conditions and failure modes. This information guides design improvements, process corrections, and component selection decisions that enhance overall product reliability.
Measurement Parameter | Typical Instrumentation | Data Collection Frequency |
Chamber Temperature | PT-100 Class A sensors | Every 1-10 seconds |
Relative Humidity | Capacitive humidity sensors | Every 10-60 seconds |
Device Power Consumption | Precision power supplies | Continuous or per cycle |
Functional Test Results | Automated test equipment | Per temperature dwell |
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards
Regulatory Requirements for Different Markets
Electronics sold internationally must satisfy diverse regulatory frameworks. European CE marking requires EMC and safety compliance testing under specified environmental conditions. Automotive suppliers must meet IATF 16949 quality system requirements including environmental stress testing protocols. Medical devices follow FDA guidance and ISO 13485 standards mandating extensive validation documentation.
Calibration and Measurement Traceability
Accurate test results depend on properly calibrated chamber instrumentation. Temperature and humidity sensors require periodic calibration traceable to national standards like NIST. Calibration certificates document measurement uncertainty and confirm chamber performance meets specification. ISO/IEC 17025 accredited calibration laboratories provide internationally recognized certification supporting regulatory submissions.
Documentation and Audit Requirements
Quality management systems mandate complete test records including equipment calibration status, environmental profiles, sample identification, test results, and failure analysis reports. Traceability links individual test units to manufacturing lot codes, enabling investigation of systematic problems. Regulatory audits scrutinize testing documentation verifying proper protocol execution and data integrity.
Standard | Application Area | Key Requirements |
IEC 60068-2-14 | General electronics | Temperature cycling test parameters |
MIL-STD-810H | Military/defense | Environmental engineering considerations |
JEDEC JESD22 | Semiconductors | Component-level reliability testing |
ISO 16750 | Automotive | Road vehicle electrical/electronic equipment |
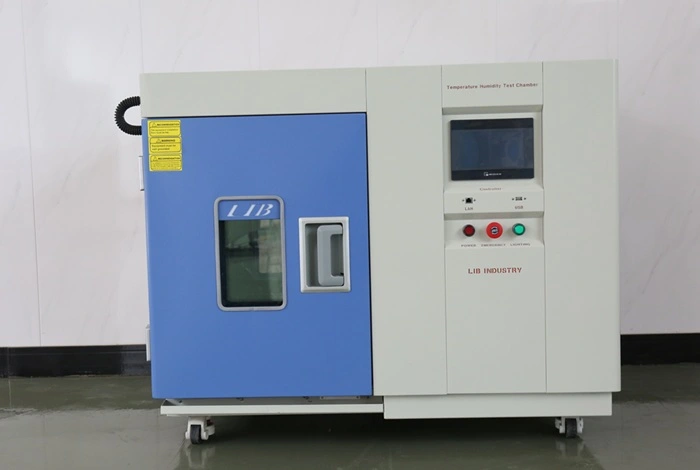
LIB Industry Calibration Environmental Chamber: Reliable Electronics Validation
Comprehensive Temperature and Humidity Control
LIB Industry calibration environmental chambers provide temperature ranges from -70°C to +150°C with ±0.5°C fluctuation precision. Humidity control spans 20% to 98% RH with ±2.5% deviation accuracy. The mechanical compression refrigeration system utilizing French TECUMSEH compressors delivers reliable cooling performance. Programmable color LCD touchscreen controllers with Ethernet connectivity enable complex profile execution and remote monitoring.
Versatile Chamber Configurations
Available volumes range from 100L benchtop units suitable for component testing to 1000L walk-in chambers accommodating complete systems. Multiple temperature ranges accommodate diverse testing requirements: A-type (-20°C to +150°C), B-type (-40°C to +150°C), and C-type (-70°C to +150°C). The 1000W heat load capacity supports testing of power-consuming electronic assemblies under realistic operating conditions.
Safety and Quality Features
Comprehensive protection systems include humidifier dry-combustion protection, over-temperature protection, over-current protection, and water shortage protection. SUS304 stainless steel interior construction resists corrosion and facilitates cleaning. Double-layer observation windows with thermostable silicone rubber sealing enable visual monitoring without compromising thermal stability. Standard cable ports allow electrical connections to test equipment while maintaining chamber integrity.
Manufacturing Excellence
ISO 9001 certification demonstrates LIB Industry's commitment to quality management throughout the manufacturing process. Compliance with international safety standards including CE, CSA, and ISO 17025 ensures global market acceptance. The automatic water purification system maintains consistent humidity generation while extending humidifier service life. Polyurethane foam and insulation cotton provide superior thermal efficiency, reducing operating costs.
Conclusion
Calibration environmental chambers represent essential tools for electronics manufacturers committed to delivering reliable products. Systematic temperature and humidity testing identifies design weaknesses, validates manufacturing processes, and ensures compliance with international standards. The comprehensive capabilities of LIB Industry chambers support diverse testing protocols from component screening to complete system qualification. Investing in proper environmental testing infrastructure reduces field failures, enhances customer satisfaction, and protects brand reputation.
FAQs
What temperature cycling profile is recommended for consumer electronics qualification?
Most consumer electronics undergo testing between -20°C and +60°C with transition rates around 1-3°C/minute. Typical protocols include 200-500 cycles with 30-minute dwells at temperature extremes. Functional testing occurs during thermal stabilization periods to verify performance across the operating range.
How does humidity affect electronic component reliability during testing?
Elevated humidity accelerates electrochemical migration between conductors, increases dielectric absorption in insulators, and promotes corrosion on metallic surfaces. The 85°C/85% RH test condition represents industry-standard accelerated humidity stress, compressing years of normal exposure into 1000-2000 test hours to reveal moisture-related failure mechanisms.
What chamber volume is appropriate for testing automotive electronic control units?
Automotive ECU testing typically requires 225L to 500L chambers providing adequate space for multiple test units plus associated wiring harnesses and monitoring equipment. Larger volumes ensure uniform temperature distribution around complex assemblies and accommodate fixtures that position units in representative mounting orientations during validation testing.
Ready to enhance your electronics testing capabilities? LIB Industry, a leading calibration environmental chamber manufacturer and supplier, delivers turn-key environmental testing solutions tailored to your specific requirements.
Contact our team at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss your application needs and discover how our chambers can validate your electronic products' reliability.