How Dust Proof Test Chambers Ensure Product Sealing Performance?
In today’s competitive market, ensuring product reliability is more important than ever. Even minimal dust exposure can compromise performance, reduce lifespan, and cause unexpected failures. Dust test chambers provide manufacturers with a controlled, precise environment to assess how products withstand dust, helping guarantee durability, safety, and consistent quality in real-world conditions.
Our Dust Proof Test Chambers have received strong praise from clients, including a U.S.-based lighting company, which highlighted that their chamber “delivered dependable performance.” This feedback underscores the reliability of our equipment in actual testing scenarios. By leveraging these chambers, manufacturers can effectively evaluate dust resistance, uncover potential weaknesses, and make necessary improvements—ensuring that products are durable, safe, and ready for the market.

Product sealing performance determines whether electronic devices, automotive components, and industrial equipment can withstand harsh environmental conditions. Dust proof test chambers replicate real-world dust exposure scenarios, allowing manufacturers to validate seal integrity before market release. These specialized testing environments simulate particle intrusion patterns that stress gaskets, enclosures, and protective barriers. By exposing products to controlled dust concentrations ranging from 2 to 4 kg/m³, engineers identify weak points in sealing designs and verify compliance with international standards like IEC 60529 and ISO 20653, ultimately preventing costly field failures and warranty claims.
Why Product Sealing Performance Matters?
Protection Against Environmental Contamination
Modern industrial environments expose products to abrasive particles, fine powders, and airborne contaminants that compromise internal mechanisms. Effective sealing systems create physical barriers preventing dust accumulation on sensitive circuitry, optical components, and mechanical assemblies. Manufacturing facilities, construction sites, and outdoor installations generate particulate matter that infiltrates inadequately sealed products, causing premature degradation.
mechanisms. Effective sealing systems create physical barriers preventing dust accumulation on sensitive circuitry, optical components, and mechanical assemblies. Manufacturing facilities, construction sites, and outdoor installations generate particulate matter that infiltrates inadequately sealed products, causing premature degradation.
Financial Implications of Sealing Failures
Warranty claims resulting from dust-related malfunctions cost manufacturers substantial resources in replacement parts, logistics, and brand reputation damage. Sealing defects discovered post-production require expensive recalls and engineering redesigns. Products lacking verified dust resistance face restricted market access in regions with stringent environmental protection requirements.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
International markets demand specific Ingress Protection (IP) ratings that certify resistance to solid particle intrusion. Automotive electronics require IP6X certification, while industrial control panels need documented proof of dust exclusion capabilities. Achieving these certifications necessitates systematic validation through standardized testing protocols that dust proof test chambers provide.
Dust Intrusion and Its Impact on Product Functionality
Mechanical Component Degradation
Particulate matter acts as an abrasive agent between moving surfaces, accelerating wear on bearings, shaft seals, and rotating assemblies. Dust particles smaller than 50 micrometers penetrate microscopic gaps, mixing with lubricants to form abrasive pastes that increase friction coefficients. This contamination reduces operational lifespans of motors, actuators, and precision mechanisms.
than 50 micrometers penetrate microscopic gaps, mixing with lubricants to form abrasive pastes that increase friction coefficients. This contamination reduces operational lifespans of motors, actuators, and precision mechanisms.
Electrical System Compromises
Conductive dust particles create unintended electrical pathways across circuit boards, causing short circuits and signal interference. Non-conductive particles accumulate on connector contacts, increasing electrical resistance and generating heat at connection points. Thermal cycling combined with dust buildup accelerates corrosion processes on exposed metal surfaces.
Optical and Sensor Malfunctions
Camera lenses, photoelectric sensors, and display screens lose functionality when dust accumulates on optical surfaces. Even minimal particle deposition reduces light transmission, affecting measurement accuracy and visibility. Cleaning procedures for sealed optical assemblies often require complete disassembly, making prevention through effective sealing economically superior.
Testing Sealing Components under Controlled Conditions
Establishing Baseline Environmental Parameters
Dust proof test chambers maintain ambient to +50℃ temperature ranges while controlling dust concentration with precision. The test environment eliminates variables present in outdoor testing, ensuring reproducible results across multiple validation cycles. Programmable controllers adjust blowing duration from 0 to 99 hours and 59 minutes, matching specific exposure scenarios.
Test Parameter | Range | Purpose |
Temperature | Ambient ~ +50℃ | Simulates thermal expansion effects on seals |
Dust Concentration | 2 ~ 4 kg/m³ | Replicates severe dust exposure conditions |
Test Duration | 0 ~ 99H59M | Validates long-term sealing effectiveness |
Monitoring Intrusion Pathways
Engineers position test specimens inside 800L to 1000L internal chambers, exposing all surfaces to circulating dust particles. Observation windows with dust scrapers allow real-time monitoring of particle behavior around joints, seams, and access panels. Vacuum systems equipped with pressure gauges verify pressure differentials that drive particle penetration.
Documentation and Traceability
Programmable color LCD touch screen controllers with Ethernet connectivity enable automated data logging throughout test cycles. This digital documentation creates verifiable records for quality management systems and regulatory submissions. PC link capabilities facilitate immediate analysis of temperature, pressure, and timing parameters.
Accelerated Sealing Stress Tests
Pressure Differential Simulation
Adjustable pressure settings in three gears create differential forces that push particles through potential leak paths. These pressure variations replicate operational conditions where internal enclosure pressures differ from external environments. Specimens experiencing cycling pressure loads reveal seal degradation patterns invisible under static conditions.
Thermal Cycling Integration
Nichrome heating elements raise dust proof test chamber temperatures while maintaining controlled dust circulation, subjecting seals to simultaneous thermal and particulate stress. Material expansion coefficients differ between seal compounds and mating surfaces, creating gaps during temperature transitions. Combined thermal and dust exposure accelerates aging processes that occur gradually during product lifecycles.
Extended Duration Protocols
Continuous operation capabilities exceeding 99 hours compress months of field exposure into days of laboratory testing. This temporal acceleration identifies progressive seal wear, material fatigue, and cumulative particle infiltration. Products demonstrating integrity after extended chamber exposure exhibit predictable reliability in actual deployment scenarios.
|
|
| Name | dust proof test chamber |
Workroom dimension (mm) | 800*800*800 D*W*H |
External dimension (mm) | 950*3150*1800 D*W*H |
Interior Volume (L) | 510 |
Diameter of Turntable (mm) | 600 |
Turntable loads | 20kgs Max |
Turntable Rotation Speed | 0~7r/min (Adjustable) |
Internal Diameter of IPX5 Nozzle | 6.3 mm |
Internal Diameter of IPX6 Nozzle | 12.5 mm |
Water Flow Rate IPX5/ IPX6 | 12.5L/min ±5% / 100L/min ±5% |
Controller | Programmable color LCD touch screen controller |
Ethernet connection, PC Link, USB | |
Build-in Water Tank(mm) | 370*375*950 |
View Window Size(mm) | 475*475 |

Evaluating Gaskets, O-rings, and Protective Seals
Material Compatibility Assessment
Different elastomer compounds respond uniquely to dust abrasion and thermal stress. Silicone, nitrile, and fluorocarbon seals undergo comparative testing to determine optimal material selection for specific applications. Dust particle sizes interact differently with seal surface textures, revealing material-specific vulnerabilities.
Seal Type | Typical Application | Test Focus |
Elastomeric Gaskets | Enclosure panels | Compression set resistance |
O-rings | Rotating shafts | Dynamic sealing under particle load |
Lip Seals | Bearing housings | Abrasion resistance |
Compression and Recovery Analysis
Sealing effectiveness depends on maintaining consistent compression forces across mating surfaces. Post-test measurements quantify permanent deformation (compression set) resulting from combined thermal and mechanical stress. Recovery characteristics indicate whether seals maintain sealing pressure after thermal cycling.
Surface Finish Interactions
Mating surface roughness influences seal performance as microscopic peaks and valleys provide potential particle ingress routes. Chamber testing with varying surface finishes identifies minimum smoothness requirements for reliable sealing. This data guides manufacturing specifications for machined, molded, or stamped sealing surfaces.
Predictive Analysis for Product Reliability
Failure Mode Identification
Systematic chamber testing reveals whether sealing failures result from material degradation, installation errors, or design deficiencies. Particles accumulating at specific locations indicate directional airflow patterns requiring design modifications. This diagnostic capability enables targeted improvements rather than complete redesigns.
Statistical Reliability Modeling
Multiple specimen testing generates datasets supporting Weibull analysis and other reliability prediction methodologies. Manufacturers establish confidence intervals for seal lifespans under defined environmental conditions. These statistical models inform warranty periods and maintenance scheduling recommendations.
Reliability Metric | Chamber-Derived Data | Business Application |
MTTF (Mean Time to Failure) | Extended duration test results | Warranty period determination |
Failure Rate (λ) | Population testing outcomes | Spare parts inventory planning |
Confidence Level | Statistical sample size | Risk assessment for market release |
Design Optimization Iteration
Rapid testing cycles enable engineers to evaluate seal design variations, comparing performance metrics across iterations. Parametric studies adjusting seal geometry, material durometer, or surface treatments accelerate development timelines. Validated improvements reduce development costs compared to field-failure-driven redesigns.
Predictive Analysis for Product Reliability
Correlation with Field Performance
Dust proof test chamber test results calibrate against actual deployment data, establishing correlation factors between laboratory exposure and real-world operational hours. This empirical relationship translates controlled test durations into predicted field lifespans. Manufacturers validate these correlations through ongoing field data collection from deployed products.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Sealing Investments
Enhanced sealing systems increase component costs but reduce warranty expenses and reputation risks. Chamber testing quantifies the performance improvement from upgraded seals, enabling financial modeling of seal investment returns. This data-driven approach justifies engineering investments to procurement and management teams.
Proactive Quality Control Integration
Production line sampling incorporates periodic chamber validation, detecting manufacturing process drift before widespread distribution. Batch testing identifies material lot variations or tooling wear affecting seal quality. This proactive approach prevents defective products from reaching customers.
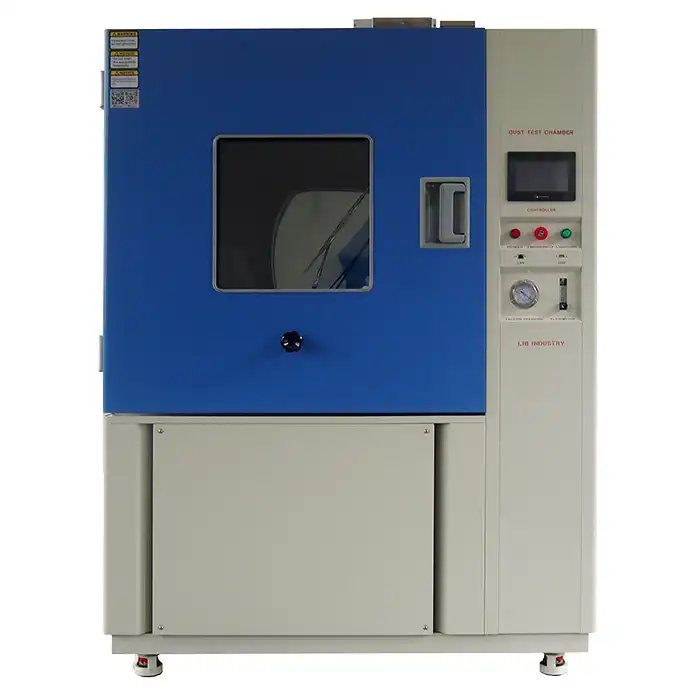
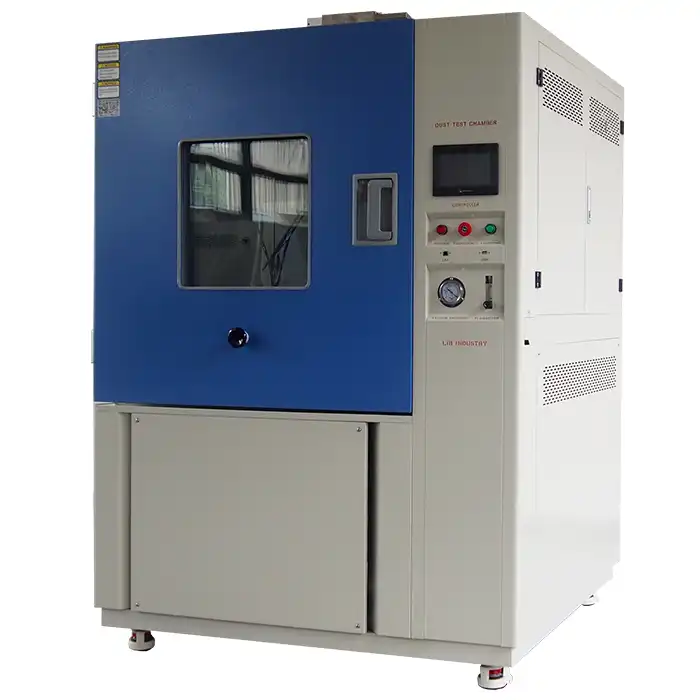
Test Sealing to Perfection with LIB Industry's Reliable Dust Proof Test Chamber
Advanced Testing Capabilities
LIB Industry's dust proof test chambers feature 304 stainless steel working rooms with electromagnetic door locks, ensuring contamination-free test environments. The dust circulation system maintains uniform particle distribution throughout the 800L to 1000L internal volumes. Maximum noise levels below 65 dBA enable placement in standard laboratory environments without specialized acoustic isolation.
Customizable Test Protocols
Programmable controllers accommodate industry-specific testing requirements, from automotive IP6X validation to electronics ingress protection certification. Dust-proof specimen power outlets rated at 16A enable testing of powered devices under operational conditions. Adjustable vacuum systems simulate altitude variations and negative pressure scenarios.
Compliance and Certification Support
Equipment designed to IEC 60529 and ISO 20653 standards ensures test results gain regulatory acceptance worldwide. CE-approved construction meets European market requirements, while comprehensive documentation supports ISO 9001 quality management integration. Technical support assists with test method development and results interpretation.
Conclusion
Dust proof test chambers transform sealing validation from subjective field observation into quantifiable laboratory science. These controlled environments accelerate product development cycles while reducing warranty risks through early detection of design vulnerabilities. Manufacturers investing in systematic sealing verification gain competitive advantages through superior product reliability and expanded market access. The integration of advanced testing capabilities, statistical analysis, and iterative design optimization establishes sealing performance as a measurable, improvable product attribute.
FAQs
What dust concentration levels replicate severe industrial environments?
Test chambers operating at 2-4 kg/m³ dust concentrations simulate extreme exposure conditions exceeding typical industrial settings. This elevated concentration accelerates testing timelines while stressing seals beyond normal operational demands, revealing potential weaknesses before field deployment.
How long should accelerated dust testing cycles run for automotive components?
Automotive sealing validation typically requires 8-24 hour continuous exposure cycles, equivalent to several months of vehicle operation. Extended protocols exceeding 48 hours validate components intended for harsh environments like construction equipment or military applications operating in desert conditions.
Can existing products undergo retroactive sealing performance validation?
Manufacturers can test production units or legacy products to establish baseline sealing performance metrics. This retroactive testing identifies improvement opportunities for next-generation designs and provides data supporting current product specifications or warranty terms.
Partner with LIB Industry for Superior Testing Solutions
As a trusted dust proof test chamber manufacturer and supplier, LIB Industry delivers turn-key environmental testing solutions globally. Our factory provides customized chambers, installation support, and comprehensive training. Contact ellen@lib-industry.com for technical specifications and quotations.