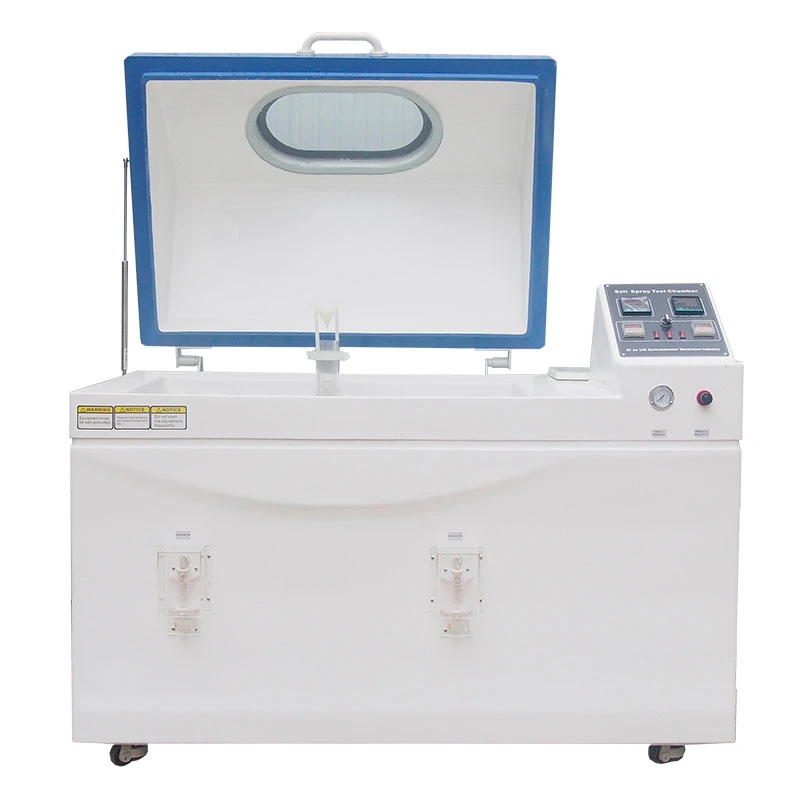
Assessing the corrosion resistance of metals, coatings, and electroplated components through real-world exposure can be a lengthy process, often requiring months or even years. Salt spray testing significantly shortens this evaluation period by creating accelerated corrosive conditions in a controlled and repeatable environment. A high-quality salt spray corrosion test chamber allows manufacturers and laboratories to obtain reliable results efficiently, while ensuring compliance with international standards such as ISO 9227, ASTM B117, ASTM G85, and JIS Z 2371.
LIB's Salt Spray Corrosion Test Chamber has gained recognition from customers across the globe for its dependable performance and ease of use. One customer, Jack, commented: "We have received and installed the chamber. Our first test panels are already running, and everything is operating smoothly." Such feedback highlights LIB's dedication to providing testing equipment that combines robust construction, user-friendly operation, and stable, repeatable testing conditions—supporting both laboratory research and industrial quality control with confidence.
Automotive coating validation relies heavily on salt spray testing to evaluate corrosion resistance under accelerated conditions. This standardized method exposes coated surfaces to a controlled saline mist environment, simulating years of real-world exposure in just weeks. Manufacturers employ salt spray test chambers to assess protective layer effectiveness, identify weaknesses in formulation or application, and ensure compliance with industry specifications. The process generates quantifiable data on coating performance, enabling engineers to optimize protective systems before mass production. By replicating harsh coastal and winter road conditions, these evaluations help automotive producers deliver vehicles that maintain appearance and structural integrity throughout their service life.
Why Corrosion Resistance Is Critical for Automotive Coatings?
Economic Impact of Coating Degradation
Premature coating breakdown generates substantial financial burdens across the automotive supply chain. Vehicle manufacturers face warranty claims, recall expenses, and brand reputation damage when protective layers fail prematurely. Estimates indicate that corrosion-related issues cost the automotive industry billions annually in remediation and lost sales. Consumers experience depreciated vehicle values and increased maintenance expenditures when protective finishes deteriorate ahead of schedule. Insurance companies process higher claim volumes for rust-related damage, affecting premium calculations across entire market segments.
warranty claims, recall expenses, and brand reputation damage when protective layers fail prematurely. Estimates indicate that corrosion-related issues cost the automotive industry billions annually in remediation and lost sales. Consumers experience depreciated vehicle values and increased maintenance expenditures when protective finishes deteriorate ahead of schedule. Insurance companies process higher claim volumes for rust-related damage, affecting premium calculations across entire market segments.
Safety Considerations in Structural Protection
Corrosion compromises more than aesthetic appeal - it threatens structural integrity and occupant safety. Critical load-bearing components depend on coating systems to prevent material degradation that could lead to catastrophic failure. Brake lines, suspension elements, and chassis members require reliable protection against environmental attack. Modern vehicle designs incorporate high-strength materials that demand specialized coating formulations to prevent galvanic corrosion at dissimilar metal interfaces. Advanced safety systems and electronic components also depend on corrosion-resistant enclosures to maintain functionality throughout the vehicle lifecycle.
Environmental Exposure Variables
Automotive coatings face diverse and aggressive environmental conditions depending on geographic location and usage patterns. Coastal regions subject vehicles to continuous salt-laden air, while northern climates introduce deicing chemicals during winter months. Industrial areas contribute acidic pollutants that accelerate coating breakdown. Temperature fluctuations create expansion and contraction cycles that stress protective layers. Humidity variations affect water vapor transmission through coating films. Understanding these exposure variables helps engineers design validation protocols that accurately predict real-world performance.
Common Automotive Coating Failure Modes Caused by Salt Exposure
Blistering and Delamination Mechanisms
Salt-induced blistering occurs when ionic species penetrate coating films and accumulate at the substrate interface. Osmotic pressure buildup causes localized lifting, creating characteristic bubble formations. These blisters eventually rupture, exposing bare metal to further attack. Delamination represents complete adhesive failure between coating layers or between coating and substrate. Poor surface preparation, contamination, or inadequate curing often contribute to reduced bond strength. Once initiated, these failure modes propagate rapidly under continued salt exposure.
buildup causes localized lifting, creating characteristic bubble formations. These blisters eventually rupture, exposing bare metal to further attack. Delamination represents complete adhesive failure between coating layers or between coating and substrate. Poor surface preparation, contamination, or inadequate curing often contribute to reduced bond strength. Once initiated, these failure modes propagate rapidly under continued salt exposure.
Undercutting and Filiform Corrosion
Undercutting describes the creeping corrosion that advances beneath intact coating films from exposed edges or defects. Salt solutions migrate along the coating-substrate interface, creating expanding zones of deterioration hidden beneath apparently sound surfaces. Filiform corrosion manifests as thread-like patterns radiating from initiation points, typically occurring under high humidity conditions. This distinctive failure mode affects aluminum substrates particularly, creating cosmetic defects that undermine customer confidence even when structural impact remains minimal.
Color Fading and Gloss Loss
Salt exposure accelerates photodegradation processes that affect coating appearance. Chloride ions catalyze oxidative reactions that break down organic binder systems, leading to chalking and color shift. Gloss reduction occurs as surface roughness increases from micro-cracking and erosion. These aesthetic failures often appear before significant protective capacity loss, yet they trigger consumer dissatisfaction and warranty claims. Pigment selection, UV stabilizer packages, and topcoat formulation significantly influence resistance to appearance degradation during salt spray exposure.
Salt Spray Test Standards for Automotive Coating Evaluation
ASTM B117 Neutral Salt Spray Protocol
ASTM B117 establishes the foundational methodology for continuous salt fog exposure testing. This standard specifies a 5% sodium chloride solution maintained at 35°C (±2°C) with pH between 6.5 and 7.2. Salt fog chamber conditions require 95-98% relative humidity and specific fog deposition rates between 1-2 mL per 80 cm² per hour. Sample positioning at 15-30 degrees from vertical ensures uniform exposure. While widely adopted, this continuous exposure method provides a baseline comparison rather than realistic cyclic conditions. Many organizations reference ASTM B117 as a minimum qualification threshold for coating systems.
ISO 9227 Variations and Extensions
ISO 9227 encompasses multiple salt spray test variations beyond neutral fog testing. The acetic acid salt spray test (AASS) employs pH-adjusted solutions to increase aggressiveness for certain coating types. Copper-accelerated acetic acid salt spray (CASS) adds cupric chloride to further intensify corrosion rates. These accelerated variants reduce test duration while maintaining correlation to field performance. ISO 9227 also addresses apparatus requirements, solution preparation, and evaluation criteria. International automotive manufacturers frequently specify ISO 9227 compliance in supplier quality agreements.
Automotive OEM-Specific Requirements
Major vehicle manufacturers develop proprietary test protocols that extend beyond general industry standards. These specifications often incorporate cyclic exposure sequences, combining salt spray with humidity chambers, temperature cycling, and UV radiation. General Motors employs GMW14872 for cosmetic corrosion evaluation, specifying exposure duration and acceptance criteria tailored to specific vehicle platforms. Ford references FLTM BI 104-01 for coating validation with distinct requirements for different vehicle zones. Understanding these OEM-specific protocols remains essential for suppliers seeking to qualify coating systems across multiple customer bases.
Comparison of Major Salt Spray Test Standards
Standard | Solution pH | Temperature | Test Type | Typical Duration |
ASTM B117 | 6.5-7.2 | 35°C | Continuous neutral | 168-1000 hours |
ISO 9227 NSS | 6.5-7.2 | 35°C | Continuous neutral | 168-720 hours |
ISO 9227 AASS | 3.1-3.3 | 35°C | Acetic acid accelerated | 48-480 hours |
ISO 9227 CASS | 3.1-3.3 | 50°C | Copper accelerated | 24-240 hours |
GMW14872 | Cyclic varied | Varied | Multi-stage cyclic | 15-45 cycles |
Test Parameters and Exposure Cycles in Coating Validation
Chamber Configuration and Environmental Controls
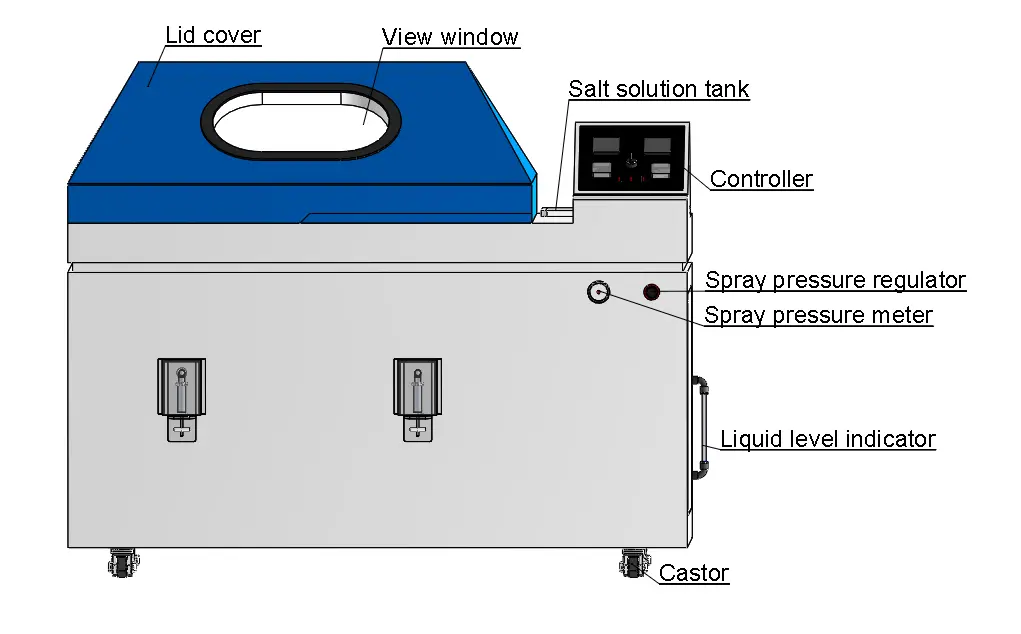
Proper salt spray test chamber setup proves critical for generating reproducible results. Internal construction utilizes glass fiber reinforced plastics or other corrosion-resistant materials to prevent contamination from chamber degradation. Atomizer towers distribute saline fog uniformly throughout the test volume, with adjustable nozzles controlling particle size and deposition rate. Air preheating systems use saturated air barrels to prevent temperature fluctuations that could affect condensation patterns. PID controllers maintain precise temperature regulation, typically within ±0.5°C. Modern systems incorporate network connectivity for remote monitoring and data logging.
Solution Preparation and Quality Control
Solution composition directly impacts test severity and reproducibility. Pharmaceutical-grade sodium chloride dissolved in distilled or deionized water prevents contamination from trace minerals. Solution pH requires regular verification and adjustment to maintain specified ranges. Fresh solution preparation at defined intervals prevents concentration drift from evaporation. Collection cups positioned throughout the chamber verify deposition rates meet standard requirements. Some advanced protocols employ conductivity monitoring to detect solution strength variations in real-time.
Cyclic Exposure Protocols
Modern automotive validation increasingly employs cyclic testing that better replicates actual service conditions. These protocols alternate salt spray exposure with dry-off periods, humidity soaking, and ambient storage phases. Cyclic testing accelerates certain degradation mechanisms absent in continuous spray methods. Temperature cycling between spray phases introduces thermal stress that exacerbates coating defects. The specific cycle architecture - duration of each phase, transition rates, and total cycle count - requires careful design based on intended application environment. Correlation studies between cyclic testing and field performance guide protocol development.
Typical Cyclic Corrosion Test Sequence
Phase | Duration | Temperature | Humidity | Purpose |
Salt Spray | 2 hours | 35°C | 95-98% | Ionic contamination |
Ambient Storage | 4 hours | 25°C | 50% | Solution penetration |
High Humidity | 2 hours | 50°C | >95% | Accelerated corrosion |
Dry-off | 16 hours | 60°C | <30% | Stress concentration |
Interpreting Coating Performance After Salt Spray Testing
Visual Assessment Methodologies
Systematic visual evaluation provides the primary metric for coating performance classification following exposure in a salt fog test chamber. Rating scales quantify defect density, blister size, and corrosion creepage from scribed areas. ASTM D714 establishes standard photographic references for blister frequency and size grading. Corrosion creep measurements determine maximum distance from deliberate defects to intact coating failure. Color difference measurements using spectrophotometry detect subtle appearance changes invisible to casual observation. Documentation through high-resolution photography enables historical comparison and trend analysis across multiple test campaigns.
Adhesion Testing Post-Exposure
Pull-off adhesion testing reveals coating-substrate bond strength degradation after salt exposure. Dolly attachment and tensile loading equipment generate quantitative adhesion values comparable to pre-exposure baselines. Cross-cut adhesion tests per ASTM D3359 assess coating cohesion and adhesion through systematic scribing and tape application. Significant reductions in measured adhesion indicate moisture infiltration or interfacial corrosion. These mechanical evaluations complement visual assessment by detecting subsurface degradation not yet manifested as visible failure.
Advanced Analytical Characterization
Sophisticated analysis techniques provide deeper insight into coating degradation mechanisms. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measures coating barrier properties through electrical resistance characterization. Scanning electron microscopy reveals microstructural changes in coating cross-sections. Energy dispersive X-ray analysis maps elemental distribution, tracking chloride penetration depth. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy identifies chemical bond degradation in organic coating systems. These analytical methods support failure analysis and coating formulation optimization programs.
Improving Automotive Coating Durability Through Corrosion Testing
Systematic Formulation Development
Salt spray validation drives iterative coating chemistry optimization throughout product development. Resin selection, crosslink density, pigment volume concentration, and additive packages undergo systematic variation and testing. Accelerated screening protocols reduce development timelines by rapidly eliminating poor-performing candidates. Statistical design of experiments methodologies optimize multiple formulation variables simultaneously. Successful formulations progress through increasingly rigorous validation protocols before field trial authorization. This systematic approach reduces warranty exposure and enhances market competitiveness.
Application Process Optimization
Coating performance depends equally on application methodology and formulation chemistry. Spray parameters including atomizing air pressure, fluid flow rate, and gun distance affect film build and uniformity. Curing temperature profiles and duration impact crosslink development and residual solvent content. Surface preparation including cleaning, conversion coating, and primer application establishes the foundation for system performance. Salt spray testing of process variations identifies optimal application windows. Quality control sampling during production verifies process capability maintenance.
Multi-Layer System Integration
Modern automotive finishes comprise multiple specialized layers working synergistically. Electrocoat primers provide corrosion resistance at the substrate interface. Surfacer layers build film thickness and appearance quality. Basecoat systems deliver color and special effects. Clearcoat topcoats protect underlying layers from environmental attack. Each layer undergoes independent validation, yet system-level testing remains essential for confirming interface compatibility. Salt spray evaluation identifies adhesion failures between layers or unexpected interactions affecting overall durability.
Automotive Coating System Layer Functions
Layer | Primary Function | Thickness Range | Key Salt Spray Performance Factors |
E-coat Primer | Substrate corrosion protection | 15-25 μm | Edge coverage, film density, curing |
Primer Surfacer | Build, adhesion promotion | 30-40 μm | Crosslink density, pigment selection |
Basecoat | Color, appearance | 12-18 μm | UV stability, moisture resistance |
Clearcoat | Environmental barrier | 35-50 μm | Chemical resistance, film integrity |
Ensure Long-Lasting Coating Durability with LIB Industry Salt Spray Test Chambers
LIB Industry manufactures precision-engineered salt spray test chambers designed specifically for demanding automotive coating validation requirements. Available volumes range from 110L compact units to 1600L production-scale systems, accommodating diverse testing needs. Temperature control from ambient to 60°C with ±0.5°C stability ensures protocol compliance across standards. Glass fiber reinforced plastic construction guarantees chamber longevity under continuous corrosive exposure. Advanced PID controllers with network connectivity enable remote monitoring and automated data collection.
| Model | S-150 | |
Internal dimensions (mm) | 470*590*400 | ||
Overall dimensions (mm) | 620*1400*1050 | ||
Temp. Range | Ambient ~ +60 degree | ||
Temp. Fluctuation | ± 0.5 ℃ | ||
Temp. Deviation | ± 2.0℃ | ||
Humidity Range | 95 % ~ 98 % RH | ||
Salt Fog Deposition | 1~2ml / 80cm2 · h | ||
Spray Type | Continuous / Periodic | ||
Heating Element | Nichrome heater | ||
Salt Fog Collected | Fog collector and fog measure cylinder | ||
Controller | PID controller | ||
Material | Glass fiber reinforced plastics | ||
Standard Configuration | 8 round bars and 7 V-shaped grooves | ||

Configuration flexibility supports both continuous and cyclic testing protocols. Adjustable spray towers and precision nozzles accommodate ASTM B117, ISO 9227, and proprietary OEM specifications. Saturated air barrel preheating systems eliminate temperature-induced artifacts. Comprehensive safety features including over-temperature protection, water shortage alarms, and earth leakage protection ensure operator safety and equipment reliability. Standard configurations include six round sample bars with five V-shaped grooves for optimized specimen positioning.
LIB Industry provides complete turnkey solutions encompassing equipment selection, installation commissioning, operator training, and ongoing technical support. Customization capabilities address unique customer requirements including specialized atmosphere control, automated specimen handling, and integrated data management systems. Global service networks ensure responsive support regardless of installation location. Selecting LIB Industry salt spray test chambers represents a strategic investment in coating quality assurance, enabling manufacturers to deliver superior corrosion protection and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Salt spray testing remains indispensable for validating automotive coating corrosion resistance before production release. Standardized protocols using specialized test chambers replicate years of environmental exposure in compressed timeframes, revealing coating vulnerabilities and guiding formulation optimization. Understanding test parameters, interpreting results accurately, and implementing improvements based on findings directly impacts vehicle durability and customer satisfaction. As coating technologies advance and environmental challenges intensify, rigorous corrosion validation continues differentiating quality manufacturers from competitors.
FAQs
How long should automotive coatings withstand salt spray testing?
Duration requirements vary by coating system and application location. Exterior body panels typically require 500-1000 hours neutral salt spray resistance, while chassis components demand 240-480 hours in accelerated protocols. Premium coating systems often exceed 1500 hours exposure with minimal degradation. Specific requirements depend on manufacturer warranties, regional exposure severity, and competitive positioning.
Can salt spray results predict actual vehicle service life?
Salt spray testing provides accelerated comparison data rather than direct service life predictions. Correlation factors between laboratory exposure and field performance depend on climate, usage patterns, and maintenance practices. Cyclic testing protocols improve correlation compared to continuous exposure methods. Manufacturers combine salt spray data with outdoor weathering, road testing, and historical warranty information for comprehensive durability predictions.
What sample preparation ensures accurate salt spray test results?
Proper surface preparation matching production processes proves critical for representative results. Cleaning removes contaminants affecting coating adhesion. Conversion coating application replicates manufacturing pretreatment. Coating application under controlled conditions eliminates variables from technique inconsistencies. Curing verification through differential scanning calorimetry confirms complete crosslinking. Edge masking prevents non-representative failure at cut edges. Following standardized preparation protocols ensures reproducibility across test campaigns.
Partner with LIB Industry for Superior Coating Validation Solutions
LIB Industry stands as a leading salt spray test chamber manufacturer and supplier, delivering precision equipment to automotive coating laboratories worldwide. Our comprehensive product line and customization capabilities ensure perfect alignment with your validation requirements. Contact our technical team at ellen@lib-industry.com to discuss your specific testing needs and discover how our chambers enhance your coating development programs.